双向链表的增删改查
1.双向链表的定义
单向链表特点:
1.我们可以轻松的到达下一个节点, 但是回到前一个节点是很难的.
2.只能从头遍历到尾或者从尾遍历到头(一般从头到尾)
双向链表特点
1.每次在插入或删除某个节点时, 需要处理四个节点的引用, 而不是两个. 实现起来要困难一些
2.相对于单向链表, 必然占用内存空间更大一些.
3.既可以从头遍历到尾, 又可以从尾遍历到头
双向链表的定义:
双向链表也叫双链表,是链表的一种,它的每个数据结点中都有两个指针,分别指向直接后继和直接前驱。所以,从双向链表中的任意一个结点开始,都可以很方便地访问它的前驱结点和后继结点。下图为双向链表的结构图。
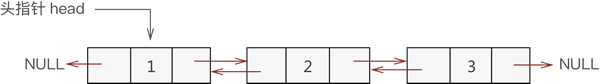
从上中可以看到,双向链表中各节点包含以下 3 部分信息:
指针域:用于指向当前节点的直接前驱节点;
数据域:用于存储数据元素。
指针域:用于指向当前节点的直接后继节点

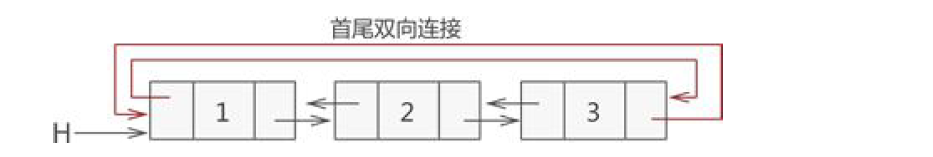
双向循环链表的定义:
双向链表也可以进行首尾连接,构成双向循环链表,如下图所示
在创建链表时,只需要在最后将收尾相连即可(创建链表代码中已经标出)。其他代码稍加改动即可。
双链表的节点结构用 C 语言实现为:
/*随机数的范围*/
#define MAX 100
/*节点结构*/
typedef struct Node{struct Node *pre;int data;struct Node *next;
}Node;2.双向链表的创建
同单链表相比,双链表仅是各节点多了一个用于指向直接前驱的指针域。因此,我们可以在单链表的基础轻松实现对双链表的创建。
需要注意的是,与单链表不同,双链表创建过程中,每创建一个新节点,都要与其前驱节点建立两次联系,分别是:
将新节点的 prior 指针指向直接前驱节点;
将直接前驱节点的 next 指针指向新节点;
这里给出创建双向链表的 C 语言实现代码:
#define MAX 100
Node *CreatNode(Node *head)
{head=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));//鍒涘缓閾捐〃绗竴涓粨鐐癸紙棣栧厓缁撶偣锛?if(head == NULL){printf("malloc error!\r\n");return NULL;}head->pre=NULL;head->next=NULL;head->data=rand()%MAX;return head;
}
Node* CreatList(Node * head,int length)
{if (length == 1){return( head = CreatNode(head));}else{head = CreatNode(head);Node * list=head;for (int i=1; iNode * body=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));body->pre=NULL;body->next=NULL;body->data=rand()%MAX;/*直接前趋结点的next指针指向新结点*/list->next=body;/*新结点指向直接前趋结点*/body->pre=list;/*把body指针给list返回*/list=list->next;}}/*加上以下两句就是双向循环链表*/// list->next=head;// head->prior=list;return head;
} 3.双向链表的插入
根据数据添加到双向链表中的位置不同,可细分为以下 3 种情况:
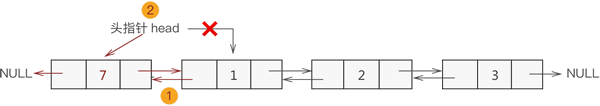
1.添加至表头
将新数据元素添加到表头,只需要将该元素与表头元素建立双层逻辑关系即可。
换句话说,假设新元素节点为 temp,表头节点为 head,则需要做以下 2 步操作即可:
temp->next=head; head->prior=temp;
将 head 移至 temp,重新指向新的表头;
将新元素 7 添加至双链表的表头,则实现过程如下图所示:
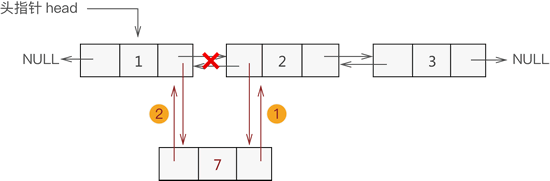
2.添加至表的中间位置
同单链表添加数据类似,双向链表中间位置添加数据需要经过以下 2 个步骤,如下图所示:
新节点先与其直接后继节点建立双层逻辑关系;
新节点的直接前驱节点与之建立双层逻辑关系;
3.添加至表尾
与添加到表头是一个道理,实现过程如下:
找到双链表中最后一个节点;
让新节点与最后一个节点进行双层逻辑关系;
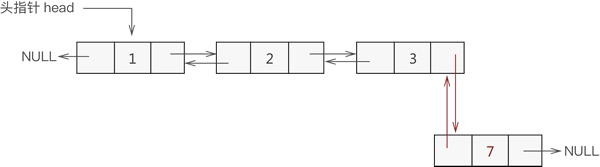
/*在第add位置的前面插入data节点*/
Node * InsertListHead(Node * head,int add,int data)
{/*新建数据域为data的结点*/Node * temp=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));if(temp== NULL){printf("malloc error!\r\n");return NULL;} else{temp->data=data;temp->pre=NULL;temp->next=NULL; }/*插入到链表头,要特殊考虑*/if (add==1){temp->next=head;head->pre=temp;head=temp;}else{Node * body=head;/*找到要插入位置的前一个结点*/for (int i=1; ibody=body->next;}/*判断条件为真,说明插入位置为链表尾*/if (body->next==NULL){body->next=temp;temp->pre=body;}else{body->next->pre=temp;temp->next=body->next;body->next=temp;temp->pre=body;}}return head;
}/*在第add位置的后面插入data节点*/
Node * InsertListEnd(Node * head,int add,int data)
{int i = 1;/*新建数据域为data的结点*/Node * temp=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));temp->data=data;temp->pre=NULL;temp->next=NULL;Node * body=head;while ((body->next)&&(ibody=body->next;i++;}/*判断条件为真,说明插入位置为链表尾*/if (body->next==NULL){body->next=temp;temp->pre=body;temp->next=NULL;}else{temp->next=body->pre->next;temp->pre=body->pre;body->next->pre=temp;body->pre->next=temp;}return head;
} 4.双向链表的删除
双链表删除结点时,只需遍历链表找到要删除的结点,然后将该节点从表中摘除即可。
例如,删除元素 2 的操作过程如图 所示:
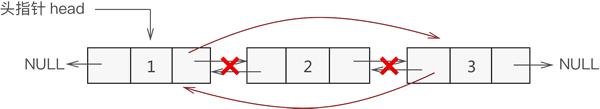
Node * DeleteList(Node * head,int data)
{Node * temp=head;/*遍历链表*/while (temp){/*判断当前结点中数据域和data是否相等,若相等,摘除该结点*/if (temp->data==data) {/*判断是否是头结点*/if(temp->pre == NULL){head=temp->next;temp->next = NULL;free(temp);return head;}/*判断是否是尾节点*/else if(temp->next == NULL){temp->pre->next=NULL;free(temp);return head;}else{temp->pre->next=temp->next;temp->next->pre=temp->pre;free(temp);return head; }}temp=temp->next;}printf("Can not find %d!\r\n",data);return head;
}5.双向链表更改节点数据
更改双链表中指定结点数据域的操作是在查找的基础上完成的。实现过程是:通过遍历找到存储有该数据元素的结点,直接更改其数据域即可。
/*更新函数,其中,add 表示更改结点在双链表中的位置,newElem 为新数据的值*/
Node *ModifyList(Node * p,int add,int newElem)
{Node * temp=p;/*遍历到被删除结点*/for (int i=1; itemp=temp->next;}temp->data=newElem;return p;
} 6.双向链表的查找
通常,双向链表同单链表一样,都仅有一个头指针。因此,双链表查找指定元素的实现同单链表类似,都是从表头依次遍历表中元素。
/*head为原双链表,elem表示被查找元素*/
int FindList(Node * head,int elem)
{
/*新建一个指针t,初始化为头指针 head*/Node * temp=head;int i=1;while (temp) {if (temp->data==elem){return i;}i++;temp=temp->next;}/*程序执行至此处,表示查找失败*/return -1;
}7.双向链表的打印
/*输出链表的功能函数*/
void PrintList(Node * head)
{Node * temp=head;while (temp) {/*如果该节点无后继节点,说明此节点是链表的最后一个节点*/if (temp->next==NULL) {printf("%d\n",temp->data);}else{printf("%d->",temp->data);}temp=temp->next;}
}测试代码
linkList.h
#include
//随机数的范围
#define MAX 100//节点结构
typedef struct Node{struct Node *pre;int data;struct Node *next;
}Node;Node* CreatNode(Node *head);//创建一个双向链表的节点
Node* CreatList(Node * head,int length);//创建一串个数为length的双向链表
void PrintList(Node * head);//输出链表的功能函数
Node * InsertListHead(Node * head,int add,int data);//在第add位置的前面插入data节点
Node * InsertListEnd(Node * head,int add,int data);//在第add位置的后面插入data节点
Node * DeleteList(Node * head,int data);//删除数据是data的节点
Node *ModifyList(Node * p,int add,int newElem);//更新函数,其中,add 表示更改结点在双链表中的位置,newElem 为新数据的值
int FindList(Node * head,int elem);//head为原双链表,elem表示被查找元素
linkList.c
#include "linkList.h"
#include
#include #define MAX 100//创建一个双向链表的节点
Node *CreatNode(Node *head)
{head=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));//申请一个链表节点的空间if(head == NULL){printf("malloc error!\r\n");return NULL;}head->pre=NULL;//指向前一个节点的指针head->next=NULL;//指向后一个节点的指针head->data=rand()%MAX;//随机数 0~100return head;
}//创建一串个数为length的双向链表
Node* CreatList(Node * head,int length)
{if (length == 1){return( head = CreatNode(head));}else{head = CreatNode(head);//先创建一个链表节点作为链表头Node * list=head;//定义一个链表指针指向该链表头for (int i=1; iNode * body = NULL;body = CreatNode(body);//再初始化一个链表节点/*直接前趋结点的next指针指向新结点*/list->next=body;//链表指针的前一个(指针)与新节点连/*新结点指向直接前趋结点*/body->pre=list;//新节点的后一个(指针)与上一个节点相连/*把body指针给list返回*/list=list->next;}}/*加上以下两句就是双向循环链表*/// list->next=head;// head->prior=list;return head;//返回该链表的链表头
}//输出链表的功能函数
void PrintList(Node * head)
{Node * temp=head;while (temp) {//如果该节点无后继节点,说明此节点是链表的最后一个节点if (temp->next==NULL) {printf("%d\n",temp->data);}else{printf("%d->",temp->data);}temp=temp->next;}
}//在第add位置的前面插入data节点
Node * InsertListHead(Node * head,int add,int data)
{//新建数据域为data的结点Node * temp=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));if(temp== NULL){printf("malloc error!\r\n");return NULL;} else{temp->data=data;temp->pre=NULL;temp->next=NULL; }//插入到链表头,要特殊考虑if (add==1){temp->next=head;head->pre=temp;head=temp;}else{Node * body=head;//找到要插入位置的前一个结点for (int i=1; ibody=body->next;}//判断条件为真,说明插入位置为链表尾if (body->next==NULL){body->next=temp;temp->pre=body;}else{body->next->pre=temp;temp->next=body->next;body->next=temp;temp->pre=body;}}return head;
}//在第add位置的后面插入data节点
Node * InsertListEnd(Node * head,int add,int data)
{int i = 1;//新建数据域为data的结点Node * temp=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));temp->data=data;temp->pre=NULL;temp->next=NULL;Node * body=head;while ((body->next)&&(ibody=body->next;i++;}//判断条件为真,说明插入位置为链表尾if (body->next==NULL){body->next=temp;temp->pre=body;temp->next=NULL;}else{temp->next=body->pre->next;temp->pre=body->pre;body->next->pre=temp;body->pre->next=temp;}return head;
}//删除数据是data的节点
Node * DeleteList(Node * head,int data)
{Node * temp=head;//遍历链表while (temp){//判断当前结点中数据域和data是否相等,若相等,摘除该结点if (temp->data==data) {//判断是否是头结点if(temp->pre == NULL){head=temp->next;temp->next = NULL;free(temp);return head;}//判断是否是尾节点else if(temp->next == NULL){temp->pre->next=NULL;free(temp);return head;}else{temp->pre->next=temp->next;temp->next->pre=temp->pre;free(temp);return head; }}temp=temp->next;}printf("Can not find %d!\r\n",data);return head;
}//更新函数,其中,add 表示更改结点在双链表中的位置,newElem 为新数据的值
Node *ModifyList(Node * p,int add,int newElem)
{Node * temp=p;//遍历到被删除结点for (int i=1; itemp=temp->next;}temp->data=newElem;return p;
}//head为原双链表,elem表示被查找元素
int FindList(Node * head,int elem)
{//新建一个指针t,初始化为头指针 headNode * temp=head;int i=1;while (temp) {if (temp->data==elem){return i;}i++;temp=temp->next;}//程序执行至此处,表示查找失败return -1;
} main.c
#include "linkList.h"int main()
{Node * head=NULL;//创建双链表head=CreatList(head,5);printf("新创建双链表为\t");PrintList(head);//在表中第 5 的位置插入元素 1head=InsertListHead(head, 5,1);printf("在表中第 5 的位置前面插入元素 1\t");PrintList(head);//在表中第 3 的位置插入元素 7head=InsertListEnd(head, 3, 7);printf("在表中第 3 的位置后面插入元素 7\t");PrintList(head);// //表中删除元素 7head=DeleteList(head, 7);printf("表中删除元素 7\t\t\t");PrintList(head);printf("元素 1 的位置是\t:%d\n",FindList(head,1));//表中第 3 个节点中的数据改为存储 6head = ModifyList(head,3,6);printf("表中第 3 个节点中的数据改为存储6\t");PrintList(head);return 0;
}测试结果

