java--IO模型
创始人
2025-05-30 07:25:00
0次
IO
- 1.IO模型的基本说明
- (1)BIO
- (2)NIO
- (3)AIO
- 2.BIO
- (1)同步阻塞演示(客户端发送数据,服务端接收数据)
- (2)多发多收机制
- (3)接收多个客户端
- (4)伪异步IO
- (5)文件上传
- (6)端口转发
- (7)即时通讯项目
- 3.NIO
- (1)三大核心(通道、缓冲区、选择器)
- (2)缓冲区(Buffer)
- 基本属性
- 常用API
- 直接与非直接缓冲区
- (3)通道(channel)
- FileChannel的常用方法
- (4)选择器(Selector)
- 选择器的应用
- 4.AIO
1.IO模型的基本说明
IO模型就是用什么样的通道或者说是通信模式和架构进行数据的传输和接收,很大程度上决定了程序通信的性能
(1)BIO
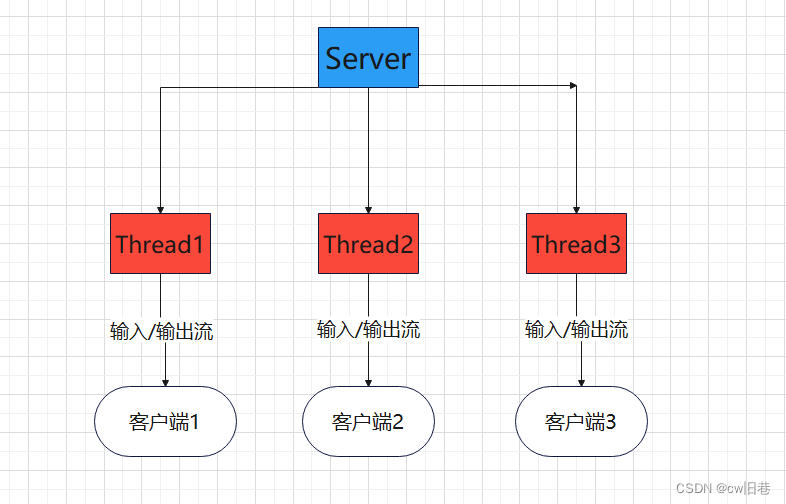
同步并阻塞(传统阻塞型),服务器实现模式为一个客户端连接一个线程,即客户端有连接请求时服务器端就需要
启动一个线程进行处理。当客户端不传送数据时,这个线程也需要等待,那么就会造成不必要的线程开销。一般适用于客户端数量较少并且固定的架构,对服务器资源的要求比较高
(2)NIO
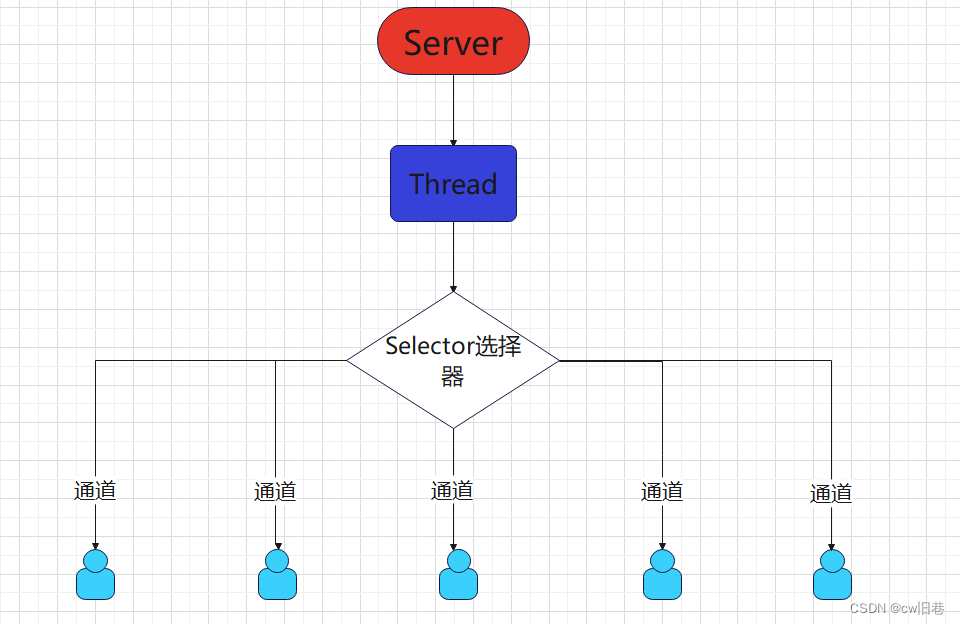
同步非阻塞,服务器实现模式为一个线程处理多个请求,即客户端发送的连接请求都会注册到多路复用器上,
多路复用器轮询到连接有IO请求就进行处理适用于连接数目多且连接比较短的架构
(3)AIO
异步非阻塞,服务器实现模式为:一个有效请求一个线程,客户端的IO请求都是由OS先完成了再通知服务器
应用去启动线程进行处理一般适用于连接数较多且连接时间较长的应用
2.BIO
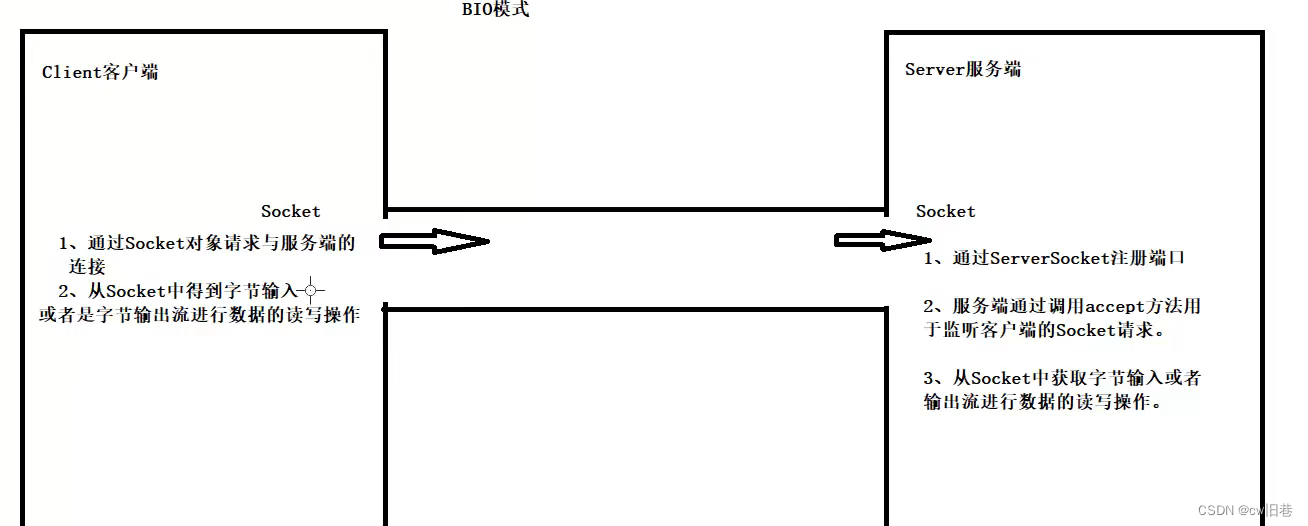
(1)同步阻塞演示(客户端发送数据,服务端接收数据)
服务端会一直等待客户端的消息,如果客户端没有进行消息的发送,服务端将一直进入阻塞状态
public class Server {public static void main(String[] args) {try {System.out.println("=======服务端启动=======");//1.定义一个ServerSocket对象进行服务端的端口注册ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(9999);//2.监听客户端的Socket连接请求Socket socket=ss.accept();//3.从socket管道中得到一个字节输入流对象InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();//4.把字节输入流包装成一个缓冲字符输入流BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is));String msg;if((msg=br.readLine())!=null){System.out.println("服务端接收到:"+msg);}} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}public class Client {public static void main(String[] args) {try {//1.创建Socket对象,请求服务端的连接Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1",9999);//2.从socket对象中获取一个字节输出流OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();//3.把字节输出流包装成一个打印流PrintStream ps=new PrintStream(os);//4.把数据发送出去ps.println("hello 你好");ps.flush();} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}finally {}}}
(2)多发多收机制
public class Server {public static void main(String[] args) {try {System.out.println("=======服务端启动=======");//1.定义一个ServerSocket对象进行服务端的端口注册ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(9999);//2.监听客户端的Socket连接请求Socket socket=ss.accept();//3.从socket管道中得到一个字节输入流对象InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();//4.把字节输入流包装成一个缓冲字符输入流BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is));String msg;while ((msg=br.readLine())!=null){System.out.println("服务端接收到:"+msg);}} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}public class Client {public static void main(String[] args) {try {//1.创建Socket对象,请求服务端的连接Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1",9999);//2.从socket对象中获取一个字节输出流OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();//3.把字节输出流包装成一个打印流PrintStream ps=new PrintStream(os);Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);while (true){System.out.print("请输入:");String msg=sc.nextLine();//4.把数据发送出去ps.println(msg);ps.flush();}} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}
(3)接收多个客户端
(1)每个Socket接收到,都会创建一个线程,线程的竞争、切换上下文影响性能(2)每个线程都会占用栈空间和CPU资源(3)并不是每个socket都进行IO操作,无意义的线程处理(4)客户端的并发访问增加时,服务端将呈现1:1的线程开销,访问量越大,系统将发生线程栈溢出,线程创建失败,最终导致进程宕机或者僵死,从而不能对外提供服务
public class ServerThreadReader extends Thread{private Socket socket;public ServerThreadReader(Socket socket){this.socket=socket;}@Overridepublic void run() {try {//从socket对象中得到一个字节输入流InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();//把字节输入流包装成一个缓冲字符输入流BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is));String msg;while ((msg=br.readLine())!=null){System.out.println("服务端接收到:"+msg);}} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}
}public class Server {public static void main(String[] args) {try {System.out.println("=======服务端启动=======");//1.定义一个ServerSocket对象进行服务端的端口注册ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(9999);//2.定义一个死循环,负责不断的接收客户端的socket连接请求while (true){Socket socket=ss.accept();//3.创建一个独立的线程来处理与这个客户端的socket通信需求new ServerThreadReader(socket).start();}} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}public class Client1 {public static void main(String[] args) {CreateClient createClient = new CreateClient();createClient.client();}}public class Client2 {public static void main(String[] args) {CreateClient createClient = new CreateClient();createClient.client();}}public class CreateClient {public void client(){try {//1.创建Socket对象,请求服务端的连接Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1",9999);//2.从socket对象中获取一个字节输出流,将其包装为打印流PrintStream ps=new PrintStream(socket.getOutputStream());//3.使用循环不断地发送消息给服务端接收Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);while (true){System.out.print("请输入要发送给服务端的数据: ");String msg=sc.nextLine();//4.把数据发送出去ps.println(msg);ps.flush();}} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}
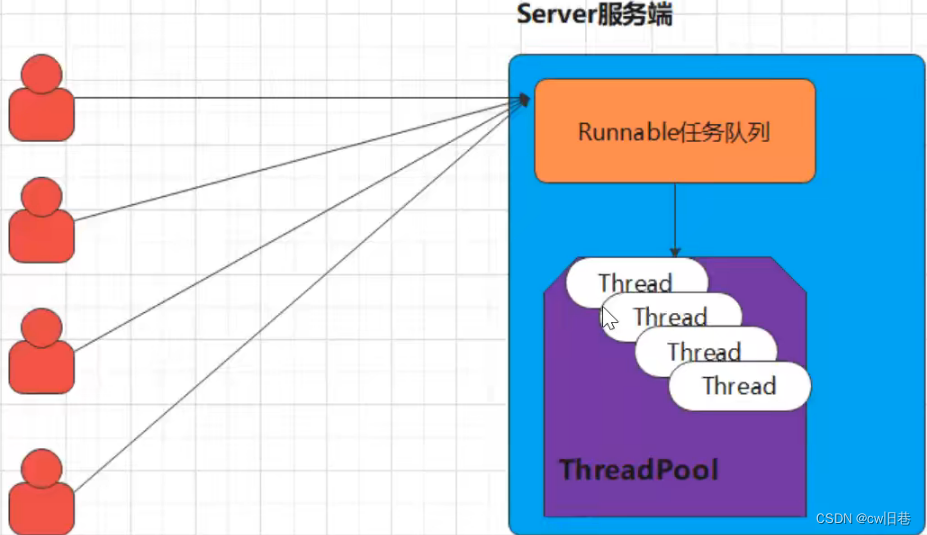
(4)伪异步IO
采用线程池和任务队列实现,当客户端接入时,将客户端的Socket封装成一个Task(该任务实现Runnable线程
任务接口)交给后端的线程池中进行处理。由于线程池可以设置任务队列的大小和最大线程数,因此,它占用的
资源是可控的,无论多少个客户端并发访问,都不会导致资源地耗尽和宕机。
public class Server {public static void main(String[] args) {try {//1.注册端口ServerSocket ss=new ServerSocket(9999);//初始化一个线程池对象HandlerSocketServerPool pool=new HandlerSocketServerPool(3,5);//2.定义一个循环接收客户端的Socket连接请求while (true){Socket socket=ss.accept();//3.把socket对象交给一个线程池进行处理//把socket封装成一个任务对象交给线程池处理Runnable target=new ServerRunnableTarget(socket);pool.execute(target);}} catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}public class ServerRunnableTarget implements Runnable{private Socket socket;public ServerRunnableTarget(Socket socket){this.socket=socket;}@Overridepublic void run() {//处理接收到客户端Socket通信需求try {//从socket对象中得到一个字节输入流InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();//把字节输入流包装成一个缓冲字符输入流BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is));String msg;while ((msg=br.readLine())!=null){System.out.println("服务端接收到:"+msg);}} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}public class HandlerSocketServerPool {//1.创建一个线程池的成员变量,用于存储一个线程池对象//ExecutorService是一个线程池接口,主要负责任务执行管理private ExecutorService executorService;//2.初始化线程池对象//参数列表:核心线程数 最大线程数 非核心线程存活时间 时间单位 阻塞队列public HandlerSocketServerPool(int maxThreadNums,int queueSize){executorService=new ThreadPoolExecutor(3, maxThreadNums,120, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(queueSize));}//3.提供一个方法来提交任务给线程池的任务队列来暂存,等着线程池来处理public void execute(Runnable target){executorService.execute(target);}
}public class Client {public static void main(String[] args) {CreateClient createClient = new CreateClient();createClient.client();}}public class CreateClient {public void client(){try {//1.创建Socket对象,请求服务端的连接Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1",9999);//2.从socket对象中获取一个字节输出流,将其包装为打印流PrintStream ps=new PrintStream(socket.getOutputStream());//3.使用循环不断地发送消息给服务端接收Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);while (true){System.out.print("请输入要发送给服务端的数据: ");String msg=sc.nextLine();//4.把数据发送出去ps.println(msg);ps.flush();}} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}
(5)文件上传
public class Service {public static void main(String[] args) {try{ServerSocket ss=new ServerSocket(9999);while (true){Socket socket=ss.accept();//交给一个独立的线程来处理与这个客户端的文件通信需求new ServerReaderThread(socket).start();}}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}}public class ServerReaderThread extends Thread{private Socket socket;public ServerReaderThread(Socket socket){this.socket=socket;}@Overridepublic void run() {OutputStream os=null;try {//1.得到一个数据输入流负责读取客户端发送过来的数据DataInputStream dis=new DataInputStream(socket.getInputStream());//2.读取客户端发送过来的文件类型String suffix=dis.readUTF();System.out.println("服务端已经接收到了文件类型");//3.定义一个字节输出管道,负责把客户端发来的文件数据写出去os=new FileOutputStream("D:\\io\\111\\"+ UUID.randomUUID().toString()+suffix);//4.从数据输入流中读取文件数据,写出到字节输出流中去byte[] buffer=new byte[1024];int len;while ((len=dis.read(buffer))!=-1){os.write(buffer,0,len);}System.out.println("服务端接收文件保存成功");}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}finally {try {os.close();} catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}
}public class Client {public static void main(String[] args) {try(InputStream is=new FileInputStream("D:\\img\\1.jpg");){//1.请求与服务端的Socket连接Socket socket=new Socket("127.0.0.1",9999);//2.把字节输出流包装成数据输出流DataOutputStream dos=new DataOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());//3.先发送上传文件的后缀给服务端dos.writeUTF(".jpg");//4.把文件数据发送给服务端进行接收byte[] buffer=new byte[1024];int len;while ((len=is.read(buffer))!=-1){dos.write(buffer,0,len);}dos.flush();socket.shutdownOutput();//通知服务端数据已经发送完毕}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}}
(6)端口转发
服务端将一个客户端的消息发送给其它客户端
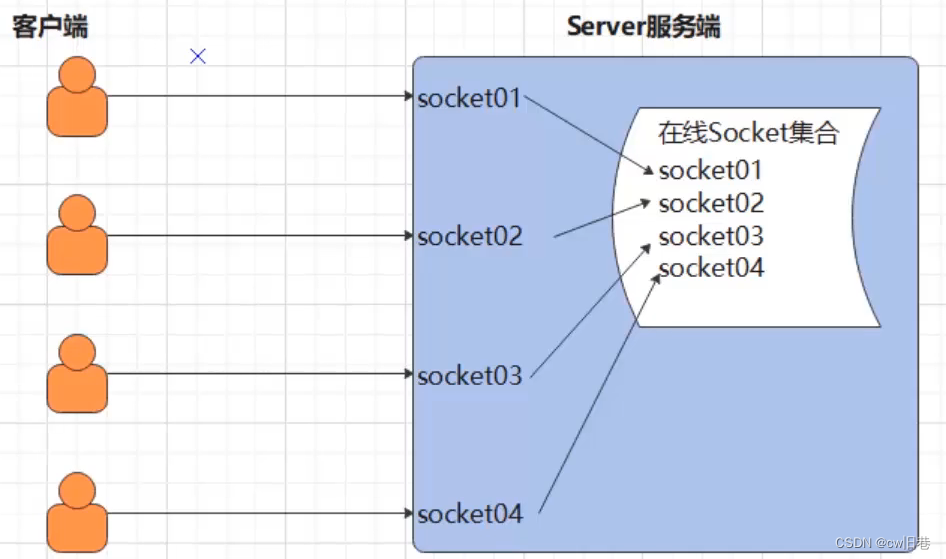
/*** BIO模式下的端口转发思想-服务端实现** 1.注册端口* 2.接收客户端的socket连接,交给一个独立的线程来处理* 3.把当前连接的客户端socket存入到一个所谓的在线socket集合中保存* 4.接收客户端的消息,然后推送给当前所有在线的socket接收*/
public class Server {//定义一个静态集合public static List allSocketOnline=new ArrayList<>();public static void main(String[] args) {try {//注册端口ServerSocket ss=new ServerSocket(9999);while (true){//可以不断地接收新的客户端//接收socketSocket socket=ss.accept();//把登录的客户端socket存入到一个在线集合中allSocketOnline.add(socket);//为当前登录成功的socket分配一个独立的线程来处理与之通信new ServerReaderThread(socket).start();}}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}}public class ServerReaderThread extends Thread{private Socket socket;public ServerReaderThread(Socket socket){this.socket=socket;}@Overridepublic void run() {try {//1.从socket中去获取当前客户端的输入流BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));String msg;while ((msg=br.readLine())!=null){//2.服务端接收到客户端的消息之后,需要推送给当前所有的在线socketsendMsgToAllClient(msg);}}catch (Exception e){System.out.println("当前有人下线");//从在线socket集合中移除本socketServer.allSocketOnline.remove(socket);}}//把当前客户端发来的消息推送给全部在线的socketprivate void sendMsgToAllClient(String msg) throws IOException {for (Socket sock : Server.allSocketOnline) {PrintStream ps=new PrintStream(sock.getOutputStream());ps.println(msg);//打印ps.flush();//将消息刷出去}}}
(7)即时通讯项目
解决客户端到客户端的通信
public class ServerChat {//定义一个集合存放所有在线的socket//key:socket value:这个socket的名称public static Map onLineSockets=new HashMap<>();public static void main(String[] args) {try {//注册端口号ServerSocket ss=new ServerSocket(9999);//循环一致等待所有可能的客户端连接while (true){Socket socket=ss.accept();//把客户端的socket管道单独配置一个线程来处理new ServerReader(socket).start();}}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}}public class ServerReader extends Thread{private Socket socket;public ServerReader(Socket socket){this.socket=socket;}@Overridepublic void run() {DataInputStream dis=null;try {dis=new DataInputStream(socket.getInputStream());//循环一直等待客户端的消息while (true){//读取消息类型 登录/群发/私聊/@消息int flag=dis.readInt();if (flag==1){//将当前登录的客户端socket存到在线人数集合中String name= dis.readUTF();System.out.println(name+"---->"+socket.getRemoteSocketAddress());ServerChat.onLineSockets.put(socket,name);}writeMsg(flag,dis);}}catch (Exception e){System.out.println("---有人下线了---");//从在线人数中将当前socket移除ServerChat.onLineSockets.remove(socket);try {writeMsg(1,dis);} catch (IOException ex) {throw new RuntimeException(ex);}}finally {try {dis.close();} catch (IOException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}private void writeMsg(int flag, DataInputStream dis) throws IOException {//定义一个变量存放最终的消息形式String msg=null;if (flag==1){//读取所有在线人数发给所有客户端去更新自己的在线人数列表StringBuilder rs=new StringBuilder();Collection onlineNames=ServerChat.onLineSockets.values();//判断是否存在在线人数if (onlineNames!=null&&onlineNames.size()>0){for (String name:onlineNames){rs.append(name+ Constants.SPILIT);}//去掉最后一个分隔符msg=rs.substring(0,rs.lastIndexOf(Constants.SPILIT));//将消息发送给所有的客户端sendMsgToAll(flag,msg);}} else if (flag==2||flag==3) {//读到 群发的 或者 @消息String newMsg= dis.readUTF();//消息//得到发件人String sendName=ServerChat.onLineSockets.get(socket);StringBuilder msgFinal=new StringBuilder();//时间SimpleDateFormat sdf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss EEE");if (flag==2){msgFinal.append(sendName).append(" ").append(sdf.format(System.currentTimeMillis()*2)).append("\r\n");msgFinal.append(" ").append(newMsg).append("\r\n");sendMsgToAll(flag,msgFinal.toString());} else if (flag==3) {msgFinal.append(sendName).append(" ").append(sdf.format(System.currentTimeMillis()*2)).append("对您私发\r\n");msgFinal.append(" ").append(newMsg).append("\r\n");//私发//得到给谁发送String destName= dis.readUTF();sendMsgToOne(destName,msgFinal.toString());}}}private void sendMsgToOne(String destName, String msg) throws IOException {//拿到所有的在线socket管道 给这些管道写出消息Set allOnlineSockets=ServerChat.onLineSockets.keySet();for (Socket sk:allOnlineSockets){//得到当前需要私发的socket//只对这个名字对应的socket私发消息if (ServerChat.onLineSockets.get(sk).trim().equals(destName)){DataOutputStream dos=new DataOutputStream(sk.getOutputStream());dos.writeInt(2);//消息类型dos.writeUTF(msg);dos.flush();}}}private void sendMsgToAll(int flag, String msg) throws IOException {//拿到所有的在线socket管道 给这些管道写出消息Set allOnlineSockets=ServerChat.onLineSockets.keySet();for (Socket sk:allOnlineSockets){DataOutputStream dos=new DataOutputStream(sk.getOutputStream());dos.writeInt(flag);dos.writeUTF(msg);dos.flush();}}}public class Constants {public static final int PORT=7778;//协议分隔符public static final String SPILIT="$%&12&";}
3.NIO
(1)NIO支持面向缓冲区的、基于通道的IO操作,以更加高效的方式进行文件的读写操作。(2)可以理解为非阻塞IO(3)以块的方式处理数据,效率高
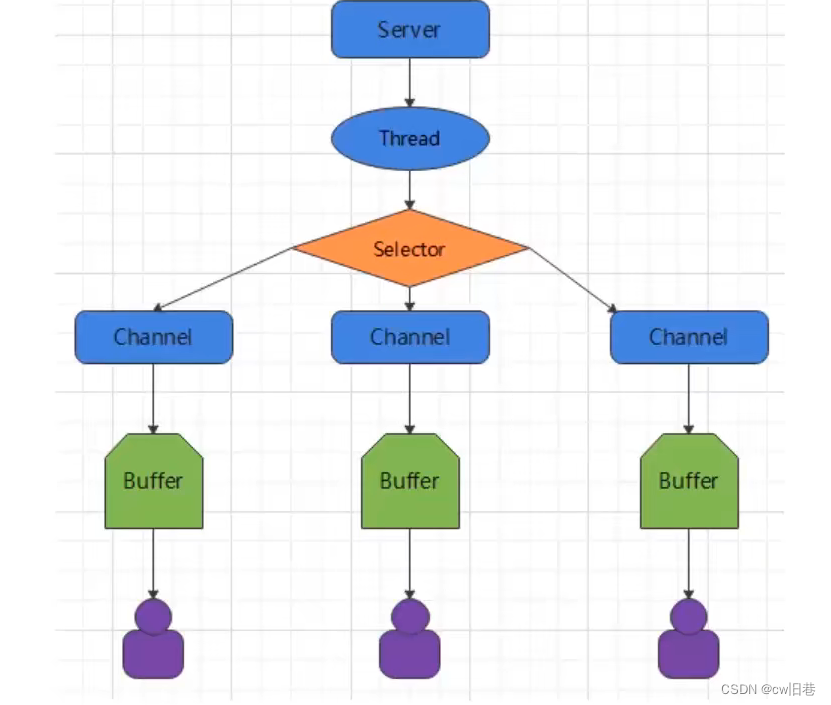
(1)三大核心(通道、缓冲区、选择器)
(1)缓冲区:本质是一块可以写入数据,然后可以从中读取数据的内存。这块内存被包装成NIO Buffer对象,并提供了一组方法,用来方便访问该块内存。(2)通道:既可以从通道中读取数据,又可以写数据到通道。通道可以非阻塞读取和写入通道,通道可以支持读取或写入缓冲区,也支持异步的读写(3)选择器:可以检查一个或多个NIO通道,并确定哪些通道已经准备好进行读取或写入。一个单独的线程可以管理多个通道,从而管理多个网络连接,提高效率。
(2)缓冲区(Buffer)
(1)保存基本数据类型
基本属性
(1)容量(capacity):作为一个内存块,Buffer具有一定的固定大小,也称为容量,缓冲区容量不能为负,并且创建后不能更改(2)限制(limit):表示缓冲区中可以操作数据的大小(limit后的数据不能进行读写)。缓冲区的限制不能为负,并且不能大于其容量。写入模式:限制等于Buffer的容量;读取模式:limit等于写入的数据量(3)位置(position):下一个要读取或写入的数据的索引,位置不能为负并且不能大于其限制(4)标记(mark)与重置(reset):标记是一个索引,通过Buffer中的mark()指定Buffer中一个特定的position,之后可以通过调用reset()方法恢复到这个position0 <= mark <= position <= limit <= capacity
常用API
(1)XxxBuffer.allocate(10):分配一个Xxx类型的缓冲区,容量设置为10XxxBuffer可以是ByteBuffer、CharBuffer、DoubleBuffer、FloatBuffer、IntBuffer、LongBuffer、 ShortBuffer、MappedByteBuffer
(1)clear():清空缓冲区并返回对缓冲区的引用(2)flip():将缓冲区的界限设置为当前位置,并将当前位置设置为0(3)capacity():返回缓冲区的大小(4)hasRemaining():判断缓冲区中是否还有元素(5)limit():返回缓冲区的界限位置(6)mark():对缓冲区设置标记(7)position():返回缓冲区的当前位置(8)position(int n):设置缓冲区的当前位置为n,并返回修改后的Buffer对象(9)remaining():返回position和limit之间的元素个数(10)reset():将位置position转到以前设置mark所在位置(11)rewind():将位置设为0,取消设置的mark(12)get():获取缓冲区中的数据get():读取单个字节get(byte[] dst):批量读取多个字节到dst中get(int index):读取指定索引位置的字节(不会移动position)(13)put():放入数据到缓冲区中put(byte b):将给定单个字节写入缓冲区的当前位置put(byte[] src):将src中的字节写入缓冲区的当前位置put(int index,byte b):将指定字节写入缓冲区的索引位置(不会移动position)
直接与非直接缓冲区
(1)直接内存缓冲区:使用 XxxBuffer.allocateDirect(1024) 来分配的缓冲区就在直接内存可以使用 isDirect() 来确定是否是直接缓冲区, 如果返回true的话就是直接缓冲区(2)直接缓冲区:基于直接内存(非堆内存),JVM将在IO操作上具有更高的性能,因为它直接作用于本地系统的IO操作。本地IO -> 直接内存 -> 本地IO(3)非直接缓冲区:基于堆内存,如果要做IO操作,会先从本进程内存复制到直接内存,再利用本地IO处理本地IO -> 直接内存 -> 堆内存 -> 直接内存 -> 本地IO (4)在做IO处理时,比如网络发送大量数据时,直接内存具有更高的效率。但是它比申请普通的堆内存需要耗费更高的性能。所以当有很大的数据需要缓存,并且生命周期又很长,或者需要频繁的IO操作(比如网络并发场景)那么就比较适合使用直接内存
(3)通道(channel)
(1)channel本身不能直接访问数据,channel只能与Buffer进行交互(2)通道可以同时进行读写,而流只能读或者只能写(3)通道可以实现异步读写数据(4)通道可以从缓冲区读数据,也可以写数据到缓冲(5)channel在NIO中是一个接口,需要使用它的实现类FileChannel:用于读取、写入、映射和操作文件的通道DatagramChannel:通过UDP读写网络中的数据通道SocketChannel:通过TCP读写网络中的数据ServerSocketChannel:可以监听新进来的TCP连接,对每一个新进来的连接都会创建一个ServerSocketChannel
FileChannel的常用方法
(1)read(ByteBuffer dst):从channel中读取数据到ByteBuffer(2)read(ByteBuffer[] dsts):将channel中的数据分散到ByteBuffer[](3)write(ByteBuffer src):将ByteBuffer 中的数据写入到channel中(4)write(ByteBuffer[] srcs):将ByteBuffer[] 中的数据聚集到channel(5)position():返回此通道的文件位置(6)FileChannel position(long p):设置此通道的文件位置(7)size():返回此通道的文件的当前大小(8)FileChannel truncate(long s):将此通道的文件截取为给定大小(9)force(boolean metaData):强制将所有对此通道的文件更新写入到存储设备中(10)transferFrom(原通道,开始位置,大小):从哪个通道复制数据transferTo(开始位置,大小,目标通道):将数据写入哪个通道
public class Test1 {//写数据到文件中@Testpublic void write(){try {//1.定义一个字节输出流通向目标文件FileOutputStream os=new FileOutputStream("hello.txt");//2.得到字节输出流对应的channelFileChannel channel = os.getChannel();//3.分配缓冲区ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);//4.将数据写入缓冲区buffer.put("hello,welcome to China".getBytes());//5.把缓冲区切换为写出模式buffer.flip();//6.将缓冲区的数据写入到通道中channel.write(buffer);channel.close();System.out.println("写入成功");} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}//从文件中读数据@Testpublic void read(){try {//1.定义一个文件输入流与源文件接通FileInputStream is=new FileInputStream("hello.txt");//2.得到字节输入流对应的channelFileChannel channel = is.getChannel();//3.分配一个缓冲区ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);//4.将数据读入缓冲区channel.read(buffer);buffer.flip();//将缓冲区的界限设置为当前位置,并将当前位置设置为0//5.读取缓冲区的数据String s=new String(buffer.array(),0,buffer.remaining());System.out.println(s);} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}//完成文件的复制@Testpublic void copy() throws Exception {//源文件File fileIn=new File("hello.txt");//源文件File fileOut=new File("hi.txt");//目的地//定义字节输入流和字节输出流FileInputStream is=new FileInputStream(fileIn);FileOutputStream os=new FileOutputStream(fileOut);//得到文件通道FileChannel isChannel = is.getChannel();FileChannel osChannel = os.getChannel();//分配缓冲区ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);while (true){//开始读取一次数据int flag = isChannel.read(buffer);//把数据读入缓冲区if (flag==-1){break;}}//已经读取了数据,把缓冲区的模式切换成可读模式buffer.flip();//从缓冲区中写出数据osChannel.write(buffer);isChannel.close();osChannel.close();System.out.println("复制成功");}/*** 分散读取:把通道中的数据读入到多个缓冲区去* 聚集写入:将多个缓冲区的数据聚集到通道中*/@Testpublic void more() throws Exception {//定义字节输入流和输出流FileInputStream is=new FileInputStream("hello.txt");FileOutputStream os=new FileOutputStream("hi.txt");//得到输入管道和输出管道FileChannel isChannel = is.getChannel();FileChannel osChannel = os.getChannel();//定义多个缓冲区做数据分散ByteBuffer buffer1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(4);ByteBuffer buffer2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);ByteBuffer[] buffers={buffer1,buffer2};//从通道中读取数据分散到各个缓冲区isChannel.read(buffers);//从每个缓冲区中查询是否有数据读取到了for (ByteBuffer buffer:buffers){buffer.flip();System.out.println(new String(buffer.array(),0,buffer.remaining()));}//聚集写入到通道osChannel.write(buffers);isChannel.close();osChannel.close();System.out.println("success");}}
(4)选择器(Selector)
(1)选择器是SelectableChannel对象的多路复用器,Selector可以同时监控多个SelectableChannel的IO状况,利用selector可使一个单独的线程管理多个通道,是非阻塞IO的核心(2)只有在通道真正有读写事件发生时,才会进行读写,就大大的减少了系统开销,并且不必为每个连接都创建一个线程,不用去维护这个线程(3)避免了多线程之间的上下文切换导致的开销
选择器的应用
//1.创建一个选择器
Selector selector=Selector.open();//2.向选择器注册通道
//2.1获取通道
ServerSocketChannel ssChannel=ServerSocketChannel.open();
//2.2切换非阻塞模式
ssChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//2.3绑定连接
ssChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(9898));
//2.4获取选择器
Selector selector=Selector.open();
//2.5将通道注册到选择器上并且指定监听接收事件
ssChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
当调用register将通道注册到选择器上时,选择器对通道的监听事件需要第二个参数指定
可以监听的事件类型:
(1)读:SelectionKey.OP_READ
(2)写:SelectionKey.OP_WRITE
(3)连接:SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT
(4)接收:SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT
若注册时不止监听一个事件,则可以使用"位或"操作符连接
4.AIO
(1)异步非阻塞,服务器实现模式为一个有效请求一个线程,客户端的IO请求都是由OS先完成了再通知
服务器应用去启动线程进行处理(2)与NIO不同,当进行读写操作时,只须直接调用API的read或write方法即可,这两种方法均为异步
的,对于读操作而言,当有流可读取时,操作系统会将可读的流传入read方法的缓冲区;对于写操作而言,
当操作系统将write方法传递的流写入完毕时,操作系统主动通知应用程序
相关内容
热门资讯
电视安卓系统哪个品牌好,哪家品...
你有没有想过,家里的电视是不是该升级换代了呢?现在市面上电视品牌琳琅满目,各种操作系统也是让人眼花缭...
安卓会员管理系统怎么用,提升服...
你有没有想过,手机里那些你爱不释手的APP,背后其实有个强大的会员管理系统在默默支持呢?没错,就是那...
安卓系统软件使用技巧,解锁软件...
你有没有发现,用安卓手机的时候,总有一些小技巧能让你玩得更溜?别小看了这些小细节,它们可是能让你的手...
安卓系统提示音替换
你知道吗?手机里那个时不时响起的提示音,有时候真的能让人心情大好,有时候又让人抓狂不已。今天,就让我...
安卓开机不了系统更新
手机突然开不了机,系统更新还卡在那里,这可真是让人头疼的问题啊!你是不是也遇到了这种情况?别急,今天...
安卓系统中微信视频,安卓系统下...
你有没有发现,现在用手机聊天,视频通话简直成了标配!尤其是咱们安卓系统的小伙伴们,微信视频功能更是用...
安卓系统是服务器,服务器端的智...
你知道吗?在科技的世界里,安卓系统可是个超级明星呢!它不仅仅是个手机操作系统,竟然还能成为服务器的得...
pc电脑安卓系统下载软件,轻松...
你有没有想过,你的PC电脑上安装了安卓系统,是不是瞬间觉得世界都大不一样了呢?没错,就是那种“一机在...
电影院购票系统安卓,便捷观影新...
你有没有想过,在繁忙的生活中,一部好电影就像是一剂强心针,能瞬间让你放松心情?而我今天要和你分享的,...
安卓系统可以写程序?
你有没有想过,安卓系统竟然也能写程序呢?没错,你没听错!这个我们日常使用的智能手机操作系统,竟然有着...
安卓系统架构书籍推荐,权威书籍...
你有没有想过,想要深入了解安卓系统架构,却不知道从何下手?别急,今天我就要给你推荐几本超级实用的书籍...
安卓系统看到的炸弹,技术解析与...
安卓系统看到的炸弹——揭秘手机中的隐形威胁在数字化时代,智能手机已经成为我们生活中不可或缺的一部分。...
鸿蒙系统有安卓文件,畅享多平台...
你知道吗?最近在科技圈里,有个大新闻可是闹得沸沸扬扬的,那就是鸿蒙系统竟然有了安卓文件!是不是觉得有...
宝马安卓车机系统切换,驾驭未来...
你有没有发现,现在的汽车越来越智能了?尤其是那些豪华品牌,比如宝马,它们的内饰里那个大屏幕,简直就像...
p30退回安卓系统
你有没有听说最近P30的用户们都在忙活一件大事?没错,就是他们的手机要退回安卓系统啦!这可不是一个简...
oppoa57安卓原生系统,原...
你有没有发现,最近OPPO A57这款手机在安卓原生系统上的表现真是让人眼前一亮呢?今天,就让我带你...
安卓系统输入法联想,安卓系统输...
你有没有发现,手机上的输入法真的是个神奇的小助手呢?尤其是安卓系统的输入法,简直就是智能生活的点睛之...
怎么进入安卓刷机系统,安卓刷机...
亲爱的手机控们,你是否曾对安卓手机的刷机系统充满好奇?想要解锁手机潜能,体验全新的系统魅力?别急,今...
安卓系统程序有病毒
你知道吗?在这个数字化时代,手机已经成了我们生活中不可或缺的好伙伴。但是,你知道吗?即使是安卓系统,...
奥迪中控安卓系统下载,畅享智能...
你有没有发现,现在汽车的中控系统越来越智能了?尤其是奥迪这种豪华品牌,他们的中控系统简直就是科技与艺...
