并发编程(一)-Thread 源码分析
创始人
2025-05-30 13:35:25
0次
一、什么是线程
线程(英语:thread)是操作系统能够进行运算调度的最小单位。它被包含在进程之中,是进程中的实际运作单位。一条线程指的是进程中一个单一顺序的控制流,一个进程中可以并发多个线程,每条线程并行执行不同的任务。在Unix System V及SunOS中也被称为轻量进程(lightweight processes),但轻量进程更多指内核线程(kernel thread),而把用户线程(user thread)称为线程。
二、线程创建方式
2.1 继承Thread
public class MyThread extends Thread{@Overridepublic void run(){}
}2.2 实现Runnable接口
public class MyThread implements Runnable(){@Overridepublic void run(){}
}2.3 实现Callable接口
public class MyThread implements Callable {@Overridepublic Integer call() throws Exception {return 0;}
} 
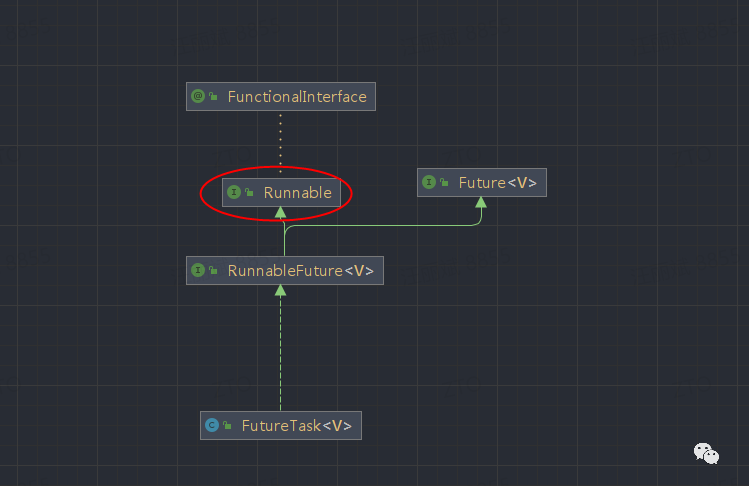
从Diagrams 图中就可得知,不管是extends Thread 还是 implements Callable接口,底层归根到底还是,实现了Runnable接口。
三、源码分析
3.1 线程中属性含义
// 线程名称
private volatile String name;
// 线程优先级
private int priority;
// 内置的Thread类
private Thread threadQ;
// JVM中的java thread 指针
private long eetop;// 是否是单步执行此线程
private boolean single_step;// 是否是守护线程
private boolean daemon = false;// jvm 状态
private boolean stillborn = false;// 构造函数中会传入的线程对象
private Runnable target;// 线程组
private ThreadGroup group;// 类加载器
private ClassLoader contextClassLoader;// 继承的访问下文
private AccessControlContext inheritedAccessControlContext;// 静态变量,使用内部静态类的单例模式,全局存在,用来生成线程名
private static int threadInitNumber;
private static synchronized int nextThreadNum() {return threadInitNumber++;
}// ThreadLocal 能为线程设置线程私有变量,设置线程上下文
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;// inheritableThreadLocals 解决子线程能够获取父线程变量
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap inheritableThreadLocals = null;// 给线程分配的栈大小,线程默认栈大小为0
private long stackSize;// 本地线程终止之后的专用状态
private long nativeParkEventPointer;// 线程id
private long tid;// 用于生成线程id,新创建线程后自增
private static long threadSeqNumber;// 线程状态,初始线程状态:0
private volatile int threadStatus = 0;// 生成线程id方法
private static synchronized long nextThreadID() {return ++threadSeqNumber;
}// LockSupport 中断
volatile Object parkBlocker;// interrupt 相关
private volatile Interruptible blocker;
private final Object blockerLock = new Object();
void blockedOn(Interruptible b) {synchronized (blockerLock) {blocker = b;}
}// 线程最低优先级
public final static int MIN_PRIORITY = 1;// 线程默认优先级
public final static int NORM_PRIORITY = 5;// 线程最高优先级
public final static int MAX_PRIORITY = 10;3.2 线程状态

public enum State {// 新建状态:Thread t = new Thread();NEW,// 运行,调用了t.start(),此时就绪(等待CPU进行调度)和运行都属于运行状态。RUNNABLE,// 阻塞,因为争用 synchronized 的 monitor 对象而发生阻塞的线程处于 blocked 状态。BLOCKED,// 等待,需要其他的线程进行唤醒。一般是调用Object.wait,Thread.join,LockSupport.parkWAITING。可以调用Object.notify,Object.notifyAll,LockSupport.unpark进行唤醒// 超时等待,可以在指定时间内自动唤醒。调用Thread.sleep(long),Object.wait(long),Thread.join(long),// LockSupport.parkNanos(long),LockSupport.parkUntil(long)等进入TIMED_WAITING状态。// 唤醒方式:时间到了,Object.notify,Object.notifyAll,LockSupport.unpark等方法TIMED_WAITING,// 终止线程的线程状态。线程已完成执行。TERMINATED;
}3.3构造方法
3.3.1 jdk1.8中Thread
3.4 init方法
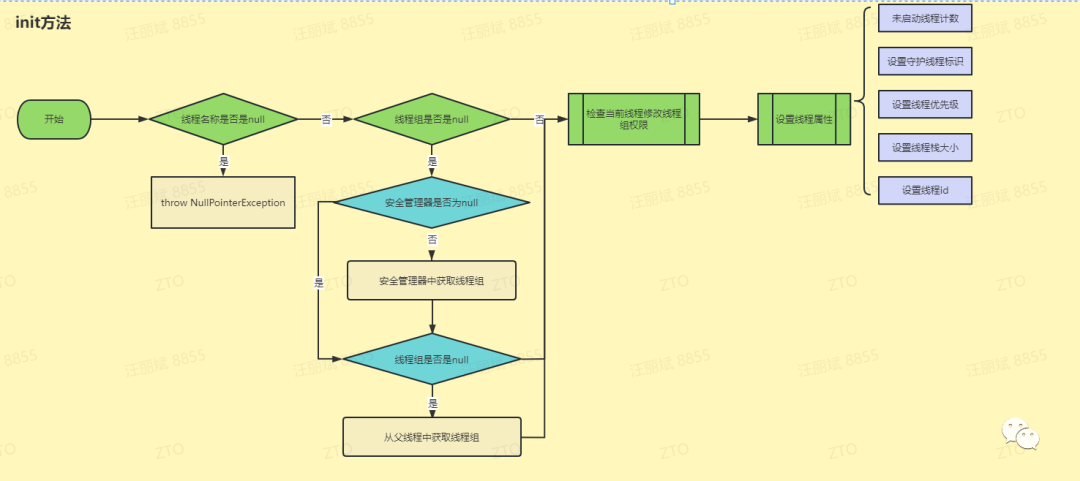
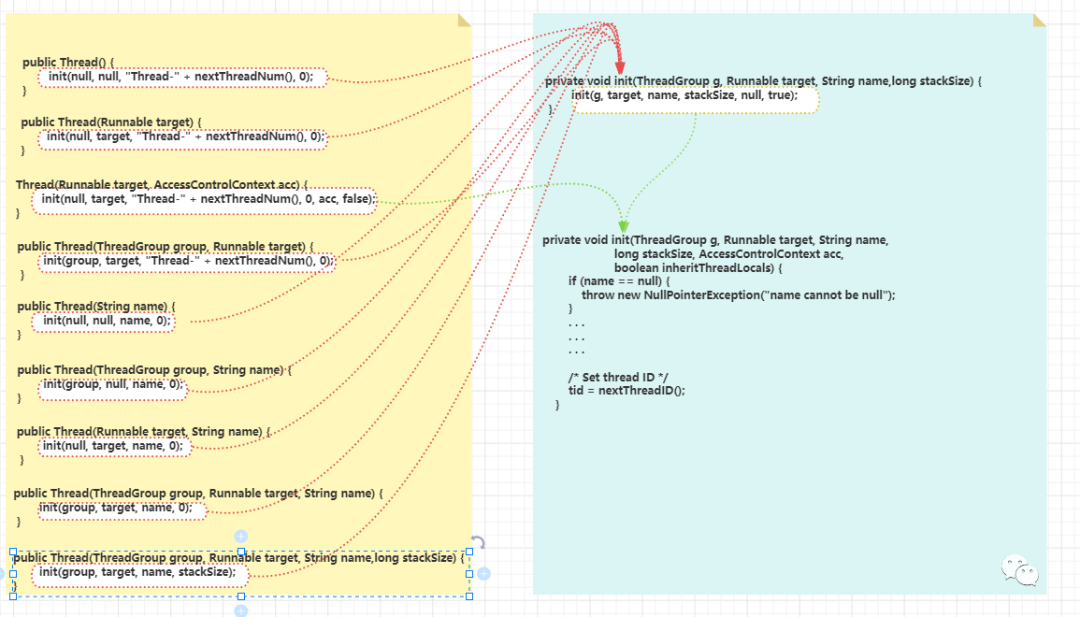
private void init(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name,long stackSize, AccessControlContext acc,boolean inheritThreadLocals) {// 线程名称校验if (name == null) {throw new NullPointerException("name cannot be null");}this.name = name;// 父线程Thread parent = currentThread();// 获取安全管理器SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();// 线程组为nullif (g == null) {// 安全管理器不为null,从安全管理器中获取线程组if (security != null) {g = security.getThreadGroup();}// 线程组为null,则从父线程中获取线程组if (g == null) {g = parent.getThreadGroup();}}// 检查当前线程拥有线程组权限g.checkAccess();if (security != null) {if (isCCLOverridden(getClass())) {security.checkPermission(SUBCLASS_IMPLEMENTATION_PERMISSION);}}// 添加未启动线程数g.addUnstarted();this.group = g;// 设置守护线程标识this.daemon = parent.isDaemon();// 获取线程优先级this.priority = parent.getPriority();// 设置类加载器if (security == null || isCCLOverridden(parent.getClass()))this.contextClassLoader = parent.getContextClassLoader();elsethis.contextClassLoader = parent.contextClassLoader; this.inheritedAccessControlContext =acc != null ? acc : AccessController.getContext();this.target = target;// 设置线程优先级setPriority(priority);if (inheritThreadLocals && parent.inheritableThreadLocals != null)// 子线程集成父线程的ThreadLocalthis.inheritableThreadLocals =ThreadLocal.createInheritedMap(parent.inheritableThreadLocals);// 设置线程栈大小this.stackSize = stackSize;// 设置线程idtid = nextThreadID();
}3.5 start方法
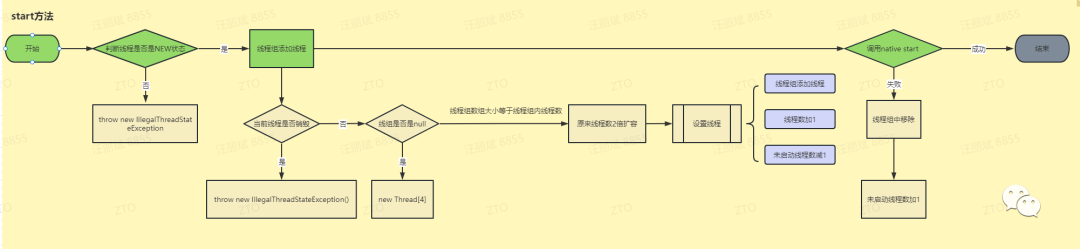
public synchronized void start() {// 检查线程状态是否是初始化状态( 0 == NEW)if (threadStatus != 0)throw new IllegalThreadStateException();// 线程组中添加该线程group.add(this);boolean started = false;try {// 调用native方法start0();// 成功启动标识started = true;} finally {try {// 没有启动成功if (!started) {// 从线程组中移除启动失败的线程group.threadStartFailed(this);}} catch (Throwable ignore) {}}
}private native void start0()3.6 run方法
public void run() {if (target != null) {// 调用构造函数Runnable的run方法target.run();}
}3.7 interrupt方法
interrupt并不是强制中断停止线程,仅仅更改线程状态。被设置中断标志的线程将继续正常运行,不受影响。
public void interrupt() {if (this != Thread.currentThread())checkAccess();synchronized (blockerLock) {Interruptible b = blocker;if (b != null) {// 设置中断状态interrupt0(); // 调用阻断程序中的中断方法b.interrupt(this);return;}}interrupt0();
}3.8 enumerate方法
// 将当前线程组及其子线程组的线程复制到指定数组中
public static int enumerate(Thread tarray[]) {return currentThread().getThreadGroup().enumerate(tarray);
}3.9 join(long millis)方法

public final synchronized void join(long millis)throws InterruptedException {long base = System.currentTimeMillis();long now = 0;// 等待毫秒数为负数,则抛出异常 if (millis < 0) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("timeout value is negative");}// 等待毫秒数等于0,会一直等待,直到线程死亡,原理就是自旋等待if (millis == 0) {while (isAlive()) {wait(0);}} else {// 等待毫秒数大于0,超出等待时间,则退出。超时自旋等待while (isAlive()) {long delay = millis - now;// 如果等待时间小于等于0,退出等待if (delay <= 0) {break;}// 调用wait方法进行线程等待wait(delay);now = System.currentTimeMillis() - base;}}
}3.10 sleep(long millis, int nanos)方法
线程休眠,线程休眠会将线程的cpu释放,但是线程占有的锁不会释放,当前线程进入Timed_waiting。
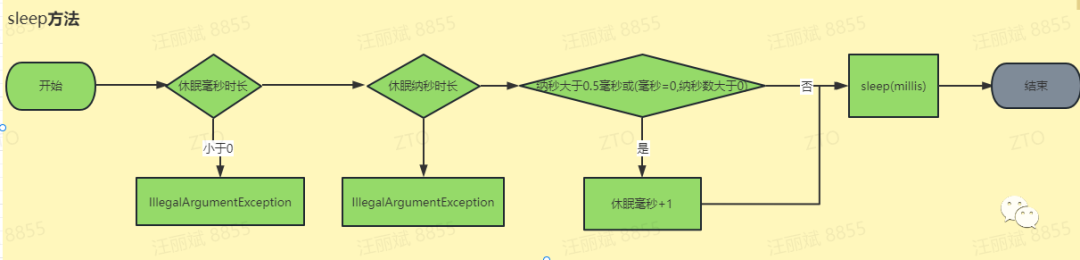
public static void sleep(long millis, int nanos)throws InterruptedException {// 睡眠毫秒实际小于0,抛出异常if (millis < 0) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("timeout value is negative");}// 睡眠纳秒时间 0~999999,if (nanos < 0 || nanos > 999999) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("nanosecond timeout value out of range");}// 1毫秒 = 1000000纳秒,纳秒数据超过一般0.5毫秒数据,就当做1毫秒,或者毫秒是0 而毫秒非零,也加1if (nanos >= 500000 || (nanos != 0 && millis == 0)) {millis++;}// 调用native方法,线程休眠sleep(millis);
}3.11 yield方法
yield是 Thread 类中的native方法,作用:让出当前线程CPU的时间片,使当前线程从执行状态变为就绪状态,cpu将会从就绪队列中重新选择一个线程,也就是说,当前线程还是有可能会被再次选择的。
相关内容
热门资讯
电视安卓系统哪个品牌好,哪家品...
你有没有想过,家里的电视是不是该升级换代了呢?现在市面上电视品牌琳琅满目,各种操作系统也是让人眼花缭...
安卓会员管理系统怎么用,提升服...
你有没有想过,手机里那些你爱不释手的APP,背后其实有个强大的会员管理系统在默默支持呢?没错,就是那...
安卓系统软件使用技巧,解锁软件...
你有没有发现,用安卓手机的时候,总有一些小技巧能让你玩得更溜?别小看了这些小细节,它们可是能让你的手...
安卓系统提示音替换
你知道吗?手机里那个时不时响起的提示音,有时候真的能让人心情大好,有时候又让人抓狂不已。今天,就让我...
安卓开机不了系统更新
手机突然开不了机,系统更新还卡在那里,这可真是让人头疼的问题啊!你是不是也遇到了这种情况?别急,今天...
安卓系统中微信视频,安卓系统下...
你有没有发现,现在用手机聊天,视频通话简直成了标配!尤其是咱们安卓系统的小伙伴们,微信视频功能更是用...
安卓系统是服务器,服务器端的智...
你知道吗?在科技的世界里,安卓系统可是个超级明星呢!它不仅仅是个手机操作系统,竟然还能成为服务器的得...
pc电脑安卓系统下载软件,轻松...
你有没有想过,你的PC电脑上安装了安卓系统,是不是瞬间觉得世界都大不一样了呢?没错,就是那种“一机在...
电影院购票系统安卓,便捷观影新...
你有没有想过,在繁忙的生活中,一部好电影就像是一剂强心针,能瞬间让你放松心情?而我今天要和你分享的,...
安卓系统可以写程序?
你有没有想过,安卓系统竟然也能写程序呢?没错,你没听错!这个我们日常使用的智能手机操作系统,竟然有着...
安卓系统架构书籍推荐,权威书籍...
你有没有想过,想要深入了解安卓系统架构,却不知道从何下手?别急,今天我就要给你推荐几本超级实用的书籍...
安卓系统看到的炸弹,技术解析与...
安卓系统看到的炸弹——揭秘手机中的隐形威胁在数字化时代,智能手机已经成为我们生活中不可或缺的一部分。...
鸿蒙系统有安卓文件,畅享多平台...
你知道吗?最近在科技圈里,有个大新闻可是闹得沸沸扬扬的,那就是鸿蒙系统竟然有了安卓文件!是不是觉得有...
宝马安卓车机系统切换,驾驭未来...
你有没有发现,现在的汽车越来越智能了?尤其是那些豪华品牌,比如宝马,它们的内饰里那个大屏幕,简直就像...
p30退回安卓系统
你有没有听说最近P30的用户们都在忙活一件大事?没错,就是他们的手机要退回安卓系统啦!这可不是一个简...
oppoa57安卓原生系统,原...
你有没有发现,最近OPPO A57这款手机在安卓原生系统上的表现真是让人眼前一亮呢?今天,就让我带你...
安卓系统输入法联想,安卓系统输...
你有没有发现,手机上的输入法真的是个神奇的小助手呢?尤其是安卓系统的输入法,简直就是智能生活的点睛之...
怎么进入安卓刷机系统,安卓刷机...
亲爱的手机控们,你是否曾对安卓手机的刷机系统充满好奇?想要解锁手机潜能,体验全新的系统魅力?别急,今...
安卓系统程序有病毒
你知道吗?在这个数字化时代,手机已经成了我们生活中不可或缺的好伙伴。但是,你知道吗?即使是安卓系统,...
奥迪中控安卓系统下载,畅享智能...
你有没有发现,现在汽车的中控系统越来越智能了?尤其是奥迪这种豪华品牌,他们的中控系统简直就是科技与艺...
