DDPG强化学习的PyTorch代码实现和逐步讲解
深度确定性策略梯度(Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient, DDPG)是受Deep Q-Network启发的无模型、非策略深度强化算法,是基于使用策略梯度的Actor-Critic,本文将使用pytorch对其进行完整的实现和讲解
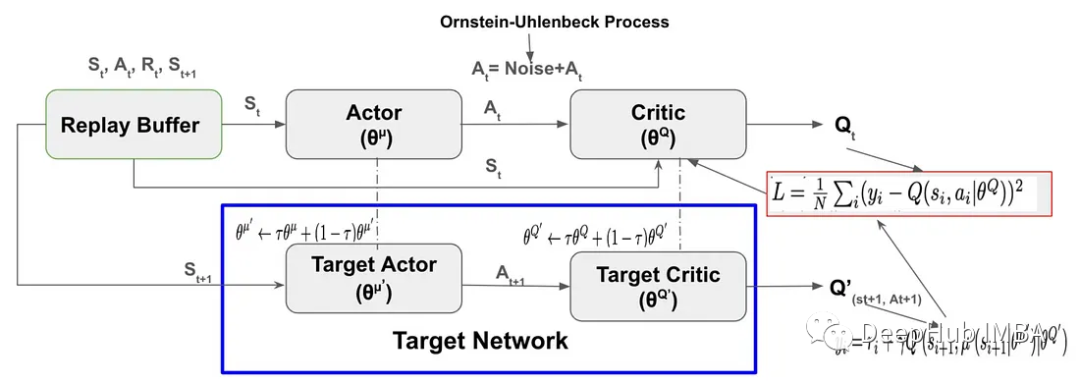
DDPG的关键组成部分是
- Replay Buffer
- Actor-Critic neural network
- Exploration Noise
- Target network
- Soft Target Updates for Target Network
下面我们一个一个来逐步实现:
Replay Buffer
DDPG使用Replay Buffer存储通过探索环境采样的过程和奖励(Sₜ,aₜ,Rₜ,Sₜ+₁)。Replay Buffer在帮助代理加速学习以及DDPG的稳定性方面起着至关重要的作用:
- 最小化样本之间的相关性:将过去的经验存储在 Replay Buffer 中,从而允许代理从各种经验中学习。
- 启用离线策略学习:允许代理从重播缓冲区采样转换,而不是从当前策略采样转换。
- 高效采样:将过去的经验存储在缓冲区中,允许代理多次从不同的经验中学习。
classReplay_buffer():'''Code based on:https://github.com/openai/baselines/blob/master/baselines/deepq/replay_buffer.pyExpects tuples of (state, next_state, action, reward, done)'''def__init__(self, max_size=capacity):"""Create Replay buffer.Parameters----------size: intMax number of transitions to store in the buffer. When the bufferoverflows the old memories are dropped."""self.storage= []self.max_size=max_sizeself.ptr=0defpush(self, data):iflen(self.storage) ==self.max_size:self.storage[int(self.ptr)] =dataself.ptr= (self.ptr+1) %self.max_sizeelse:self.storage.append(data)defsample(self, batch_size):"""Sample a batch of experiences.Parameters----------batch_size: intHow many transitions to sample.Returns-------state: np.arraybatch of state or observationsaction: np.arraybatch of actions executed given a statereward: np.arrayrewards received as results of executing actionnext_state: np.arraynext state next state or observations seen after executing actiondone: np.arraydone[i] = 1 if executing ation[i] resulted inthe end of an episode and 0 otherwise."""ind=np.random.randint(0, len(self.storage), size=batch_size)state, next_state, action, reward, done= [], [], [], [], []foriinind:st, n_st, act, rew, dn=self.storage[i]state.append(np.array(st, copy=False))next_state.append(np.array(n_st, copy=False))action.append(np.array(act, copy=False))reward.append(np.array(rew, copy=False))done.append(np.array(dn, copy=False))returnnp.array(state), np.array(next_state), np.array(action), np.array(reward).reshape(-1, 1), np.array(done).reshape(-1, 1)
Actor-Critic Neural Network
这是Actor-Critic 强化学习算法的 PyTorch 实现。该代码定义了两个神经网络模型,一个 Actor 和一个 Critic。
Actor 模型的输入:环境状态;Actor 模型的输出:具有连续值的动作。
Critic 模型的输入:环境状态和动作;Critic 模型的输出:Q 值,即当前状态-动作对的预期总奖励。
classActor(nn.Module):"""The Actor model takes in a state observation as input and outputs an action, which is a continuous value.It consists of four fully connected linear layers with ReLU activation functions and a final output layer selects one single optimized action for the state"""def__init__(self, n_states, action_dim, hidden1):super(Actor, self).__init__()self.net=nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(n_states, hidden1), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(hidden1, hidden1), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(hidden1, hidden1), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(hidden1, 1))defforward(self, state):returnself.net(state)classCritic(nn.Module):"""The Critic model takes in both a state observation and an action as input and outputs a Q-value, which estimates the expected total reward for the current state-action pair. It consists of four linear layers with ReLU activation functions, State and action inputs are concatenated before being fed into the first linear layer. The output layer has a single output, representing the Q-value"""def__init__(self, n_states, action_dim, hidden2):super(Critic, self).__init__()self.net=nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(n_states+action_dim, hidden2), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(hidden2, hidden2), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(hidden2, hidden2), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(hidden2, action_dim))defforward(self, state, action):returnself.net(torch.cat((state, action), 1))
Exploration Noise
向 Actor 选择的动作添加噪声是 DDPG 中用来鼓励探索和改进学习过程的一种技术。
可以使用高斯噪声或 Ornstein-Uhlenbeck 噪声。 高斯噪声简单且易于实现,Ornstein-Uhlenbeck 噪声会生成时间相关的噪声,可以帮助代理更有效地探索动作空间。但是与高斯噪声方法相比,Ornstein-Uhlenbeck 噪声波动更平滑且随机性更低。
importnumpyasnpimportrandomimportcopyclassOU_Noise(object):"""Ornstein-Uhlenbeck process.code from :https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/1287634/implementing-ornstein-uhlenbeck-in-matlabThe OU_Noise class has four attributessize: the size of the noise vector to be generatedmu: the mean of the noise, set to 0 by defaulttheta: the rate of mean reversion, controlling how quickly the noise returns to the meansigma: the volatility of the noise, controlling the magnitude of fluctuations"""def__init__(self, size, seed, mu=0., theta=0.15, sigma=0.2):self.mu=mu*np.ones(size)self.theta=thetaself.sigma=sigmaself.seed=random.seed(seed)self.reset()defreset(self):"""Reset the internal state (= noise) to mean (mu)."""self.state=copy.copy(self.mu)defsample(self):"""Update internal state and return it as a noise sample.This method uses the current state of the noise and generates the next sample"""dx=self.theta* (self.mu-self.state) +self.sigma*np.array([np.random.normal() for_inrange(len(self.state))])self.state+=dxreturnself.state
要在DDPG中使用高斯噪声,可以直接将高斯噪声添加到代理的动作选择过程中。
DDPG
DDPG (Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient)采用两组Actor-Critic神经网络进行函数逼近。在DDPG中,目标网络是Actor-Critic ,它目标网络具有与Actor-Critic网络相同的结构和参数化。
在训练期时,代理使用其 Actor-Critic 网络与环境交互,并将经验元组(Sₜ、Aₜ、Rₜ、Sₜ+₁)存储在Replay Buffer中。 然后代理从 Replay Buffer 中采样并使用数据更新 Actor-Critic 网络。 DDPG 算法不是通过直接从 Actor-Critic 网络复制来更新目标网络权重,而是通过称为软目标更新的过程缓慢更新目标网络权重。
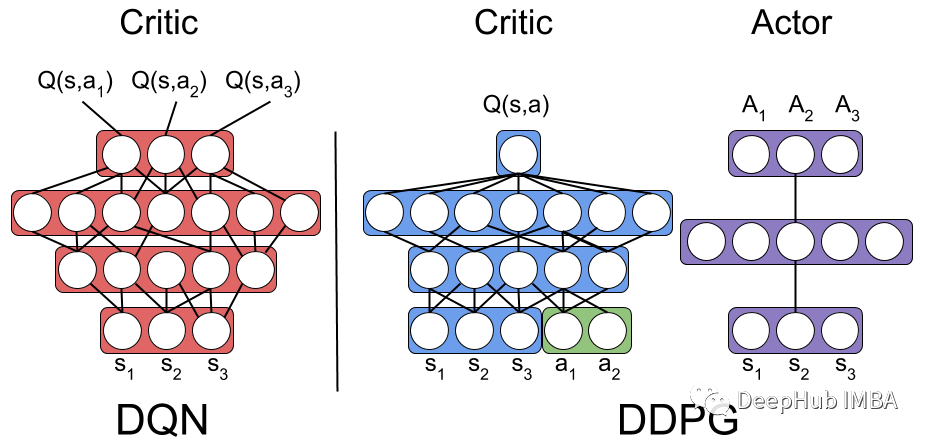
软目标的更新是从Actor-Critic网络传输到目标网络的称为目标更新率(τ)的权重的一小部分。
软目标的更新公式如下:
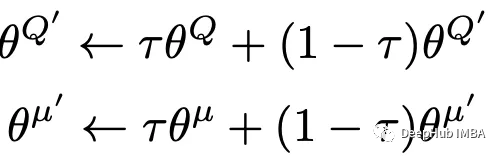
通过使用软目标技术,可以大大提高学习的稳定性。
#Set Hyperparameters# Hyperparameters adapted for performance fromcapacity=1000000batch_size=64update_iteration=200tau=0.001# tau for soft updatinggamma=0.99# discount factordirectory='./'hidden1=20# hidden layer for actorhidden2=64.#hiiden laye for criticclassDDPG(object):def__init__(self, state_dim, action_dim):"""Initializes the DDPG agent. Takes three arguments:state_dim which is the dimensionality of the state space, action_dim which is the dimensionality of the action space, and max_action which is the maximum value an action can take. Creates a replay buffer, an actor-critic networks and their corresponding target networks. It also initializes the optimizer for both actor and critic networks alog with counters to track the number of training iterations."""self.replay_buffer=Replay_buffer()self.actor=Actor(state_dim, action_dim, hidden1).to(device)self.actor_target=Actor(state_dim, action_dim, hidden1).to(device)self.actor_target.load_state_dict(self.actor.state_dict())self.actor_optimizer=optim.Adam(self.actor.parameters(), lr=3e-3)self.critic=Critic(state_dim, action_dim, hidden2).to(device)self.critic_target=Critic(state_dim, action_dim, hidden2).to(device)self.critic_target.load_state_dict(self.critic.state_dict())self.critic_optimizer=optim.Adam(self.critic.parameters(), lr=2e-2)# learning rateself.num_critic_update_iteration=0self.num_actor_update_iteration=0self.num_training=0defselect_action(self, state):"""takes the current state as input and returns an action to take in that state. It uses the actor network to map the state to an action."""state=torch.FloatTensor(state.reshape(1, -1)).to(device)returnself.actor(state).cpu().data.numpy().flatten()defupdate(self):"""updates the actor and critic networks using a batch of samples from the replay buffer. For each sample in the batch, it computes the target Q value using the target critic network and the target actor network. It then computes the current Q value using the critic network and the action taken by the actor network. It computes the critic loss as the mean squared error between the target Q value and the current Q value, and updates the critic network using gradient descent. It then computes the actor loss as the negative mean Q value using the critic network and the actor network, and updates the actor network using gradient ascent. Finally, it updates the target networks using soft updates, where a small fraction of the actor and critic network weights are transferred to their target counterparts. This process is repeated for a fixed number of iterations."""foritinrange(update_iteration):# For each Sample in replay buffer batchstate, next_state, action, reward, done=self.replay_buffer.sample(batch_size)state=torch.FloatTensor(state).to(device)action=torch.FloatTensor(action).to(device)next_state=torch.FloatTensor(next_state).to(device)done=torch.FloatTensor(1-done).to(device)reward=torch.FloatTensor(reward).to(device)# Compute the target Q valuetarget_Q=self.critic_target(next_state, self.actor_target(next_state))target_Q=reward+ (done*gamma*target_Q).detach()# Get current Q estimatecurrent_Q=self.critic(state, action)# Compute critic losscritic_loss=F.mse_loss(current_Q, target_Q)# Optimize the criticself.critic_optimizer.zero_grad()critic_loss.backward()self.critic_optimizer.step()# Compute actor loss as the negative mean Q value using the critic network and the actor networkactor_loss=-self.critic(state, self.actor(state)).mean()# Optimize the actorself.actor_optimizer.zero_grad()actor_loss.backward()self.actor_optimizer.step()"""Update the frozen target models using soft updates, where tau,a small fraction of the actor and critic network weights are transferred to their target counterparts. """forparam, target_paraminzip(self.critic.parameters(), self.critic_target.parameters()):target_param.data.copy_(tau*param.data+ (1-tau) *target_param.data)forparam, target_paraminzip(self.actor.parameters(), self.actor_target.parameters()):target_param.data.copy_(tau*param.data+ (1-tau) *target_param.data)self.num_actor_update_iteration+=1self.num_critic_update_iteration+=1defsave(self):"""Saves the state dictionaries of the actor and critic networks to files"""torch.save(self.actor.state_dict(), directory+'actor.pth')torch.save(self.critic.state_dict(), directory+'critic.pth')defload(self):"""Loads the state dictionaries of the actor and critic networks to files"""self.actor.load_state_dict(torch.load(directory+'actor.pth'))self.critic.load_state_dict(torch.load(directory+'critic.pth'))
训练DDPG
这里我们使用 OpenAI Gym 的“MountainCarContinuous-v0”来训练我们的DDPG RL 模型,这里的环境提供连续的行动和观察空间,目标是尽快让小车到达山顶。
下面定义算法的各种参数,例如最大训练次数、探索噪声和记录间隔等等。 使用固定的随机种子可以使得过程能够回溯。
importgym# create the environmentenv_name='MountainCarContinuous-v0'env=gym.make(env_name)device='cuda'iftorch.cuda.is_available() else'cpu'# Define different parameters for training the agentmax_episode=100max_time_steps=5000ep_r=0total_step=0score_hist=[]# for rensering the environmnetrender=Truerender_interval=10# for reproducibilityenv.seed(0)torch.manual_seed(0)np.random.seed(0)#Environment action ans statesstate_dim=env.observation_space.shape[0]action_dim=env.action_space.shape[0]max_action=float(env.action_space.high[0])min_Val=torch.tensor(1e-7).float().to(device) # Exploration Noiseexploration_noise=0.1exploration_noise=0.1*max_action
创建DDPG代理类的实例,以训练代理达到指定的次数。在每轮结束时调用代理的update()方法来更新参数,并且在每十轮之后使用save()方法将代理的参数保存到一个文件中。
# Create a DDPG instanceagent=DDPG(state_dim, action_dim)# Train the agent for max_episodesforiinrange(max_episode):total_reward=0step=0state=env.reset()for tinrange(max_time_steps):action=agent.select_action(state)# Add Gaussian noise to actions for explorationaction= (action+np.random.normal(0, 1, size=action_dim)).clip(-max_action, max_action)#action += ou_noise.sample()next_state, reward, done, info=env.step(action)total_reward+=rewardifrenderandi>=render_interval : env.render()agent.replay_buffer.push((state, next_state, action, reward, np.float(done)))state=next_stateifdone:breakstep+=1score_hist.append(total_reward)total_step+=step+1print("Episode: \t{} Total Reward: \t{:0.2f}".format( i, total_reward))agent.update()ifi%10==0:agent.save()env.close()
测试DDPG
test_iteration=100foriinrange(test_iteration):state=env.reset()fortincount():action=agent.select_action(state)next_state, reward, done, info=env.step(np.float32(action))ep_r+=rewardprint(reward)env.render()ifdone: print("reward{}".format(reward))print("Episode \t{}, the episode reward is \t{:0.2f}".format(i, ep_r))ep_r=0env.render()breakstate=next_state
我们使用下面的参数让模型收敛:
- 从标准正态分布中采样噪声,而不是随机采样。
- 将polyak常数(tau)从0.99更改为0.001
- 修改Critic 网络的隐藏层大小为[64,64]。在Critic 网络的第二层之后删除了ReLU激活。改成(Linear, ReLU, Linear, Linear)。
- 最大缓冲区大小更改为1000000
- 将batch_size的大小从128更改为64
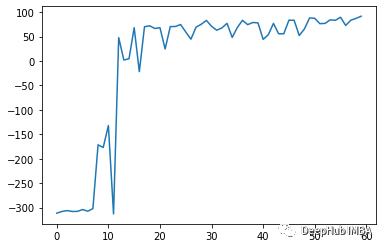
训练了75轮之后的效果如下:
总结
DDPG算法是一种受deep Q-Network (DQN)算法启发的无模型off-policy Actor-Critic算法。它结合了策略梯度方法和Q-learning的优点来学习连续动作空间的确定性策略。
与DQN类似,它使用重播缓冲区存储过去的经验和目标网络,用于训练网络,从而提高了训练过程的稳定性。
DDPG算法需要仔细的超参数调优以获得最佳性能。超参数包括学习率、批大小、目标网络更新速率和探测噪声参数。超参数的微小变化会对算法的性能产生重大影响。
上面的参数来自:
https://avoid.overfit.cn/post/9951ac196ec84629968ce7168215e461
作者:Renu Khandelwal
