jdb2/kworker
创始人
2024-05-08 12:31:13
0次
测试代码出自:块设备IO优化的典型案例分析_papaofdoudou的博客-CSDN博客_kworker/u2:2-2-
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include //O_DIRECT
#define __USE_GNU 1
#include
#include
#include
#include int fallocate(int , int , off_t, off_t);
static void write_test(int fdno)
{int origin_len;int reallen;void *mp;int len = 1 * 1024 * 1024;origin_len = len;len = len + (getpagesize() - len%getpagesize());//printf("%s line %d, len = %d.\n", __func__, __LINE__, len);unsigned char *p = malloc(len + getpagesize());if(p == NULL){printf("%s line %d, malloc failure.\n", __func__, __LINE__);return;}mp = p;unsigned char *q = (unsigned char *)(((unsigned long)p + getpagesize())&(~(getpagesize()-1)));p = q;//printf("q = %p, mp = %p.\n", q, mp);memset(p, 0x00, len);//lseek(fdno, 0, SEEK_SET);//int reallen = read(fdno, p,len);//printf("%s line %d, reallen %d read failure.er %s\n", __func__, __LINE__, reallen, strerror(errno));//printf("%s line %d, fdno = %d\n", __func__, __LINE__, fdno);//lseek(fdno, 0, SEEK_SET);reallen = write(fdno, p, origin_len);//printf("%s line %d, reallen = %d.\n", __func__, __LINE__, reallen);//lseek(fdno, 0, SEEK_SET);free(mp);mp = NULL;return;
}static void* write_thread1(void *p)
{int fdno;fdno = open("./fuck.bin", O_DIRECT|O_RDWR|O_CREAT, 0666);//fdno = open("./fuck.bin", O_RDWR|O_CREAT, 0666);if(fdno < 0){printf("%s line %d, open file failure.\n", __func__, __LINE__);return NULL;}fallocate(fdno, 1, 0, 100*1024*1024);//fallocate(fdno, 0, 0, 100*1024*1024);//return NULL;while(1){write_test(fdno);}close(fdno);return NULL;
}static void* write_thread2(void *p)
{int fdno;fdno = open("./new.bin", O_DIRECT|O_RDWR|O_CREAT, 0666);if(fdno < 0){printf("%s line %d, open file failure.\n", __func__, __LINE__);return NULL;}fallocate(fdno, 1, 0, 100*1024*1024);//fallocate(fdno, 0, 0, 100*1024*1024);//return NULL;while(1){write_test(fdno);}close(fdno);return NULL;
}int main(int argc,char **argv)
{pthread_t t1,t2;pthread_create(&t1,0,write_thread1,NULL);pthread_create(&t2,0,write_thread2,NULL);pthread_join(t1,NULL);pthread_join(t2,NULL);return 0;
} 块起始分别为9961472、9961984、9962496、9963008,每个需要512 sectiors 扇区,本次写1M的文件,需要4*512=1024个扇区,即每个扇区是1K
[281277.215000] test_emmc(14438): dirtied inode 1572868 (fuck.bin) on mmcblk0
[281277.215000] test_emmc(14438): WRITE block 9961472 on mmcblk0 (512 sectors)
[281277.215000] test_emmc(14438): WRITE block 9961984 on mmcblk0 (512 sectors)
[281277.219000] test_emmc(14438): WRITE block 9962496 on mmcblk0 (512 sectors)
[281277.220000] test_emmc(14438): WRITE block 9963008 on mmcblk0 (512 sectors)
[281283.008000] jbd2/mmcblk0-8(833): WRITE block 29730136 on mmcblk0 (8 sectors)
[281283.008000] jbd2/mmcblk0-8(833): WRITE block 29730144 on mmcblk0 (8 sectors)
[281283.013000] jbd2/mmcblk0-8(833): WRITE block 29730152 on mmcblk0 (8 sectors)
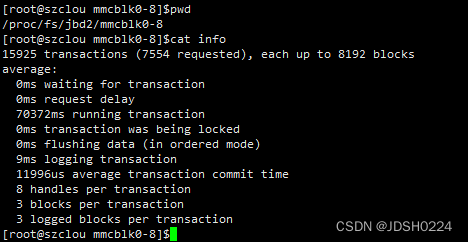
[281284.018000] kworker/u2:0(14315): WRITE block 50331904 on mmcblk0 (8 sectors)问题1:jbd2/mmcblk0-8和kworker/u2:0有什么差别?
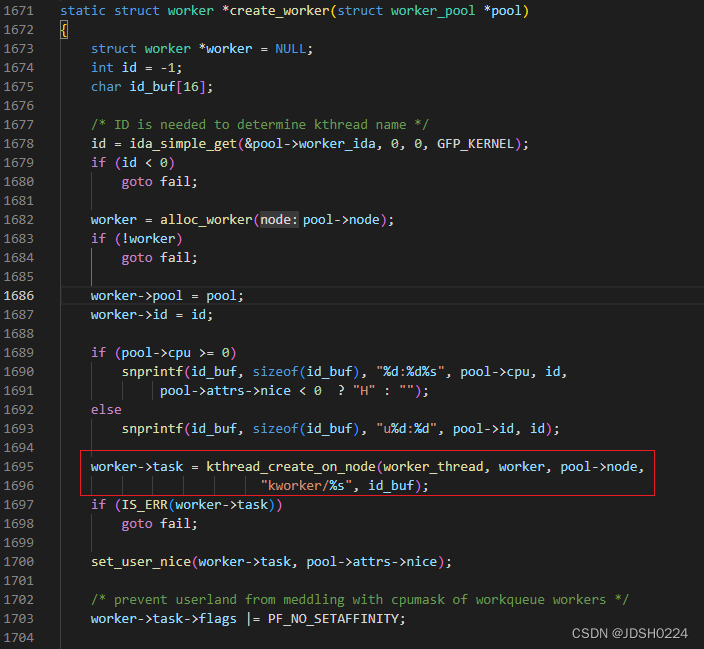
kworker线程创建
路径:kernel\workqueue.c
JBD2(journaling block device 2)
关于JBD介绍:https://help.aliyun.com/document_detail/155605.html
JDB的工作原理
JBD2(journaling block device 2)系统分析(一)-dessasic-ChinaUnix博客
性能分析之解决 jbd2 引起 IO 高问题_zuozewei的博客-CSDN博客
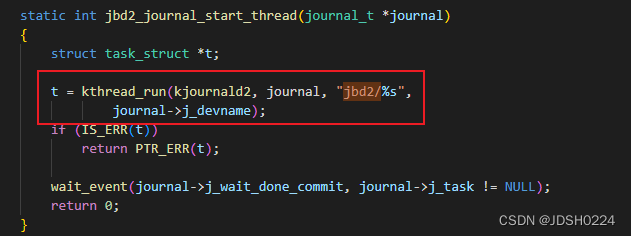
JDB2线程创建
[root@szclou mmcblk0-8]$ps -aux | grep jbd*
root 833 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S Jan04 0:06 [jbd2/mmcblk0-8]
root 14546 0.0 0.3 1860 876 pts/2 S+ 14:49 0:00 grep jbd*
JBD2源代码路径:fs\jbd2\journal.c
某大神发现jbd2日志更新时会引发io访问100%,是内核代码有bug,链接:性能分析之解决 jbd2 引起 IO 高问题_zuozewei的博客-CSDN博客
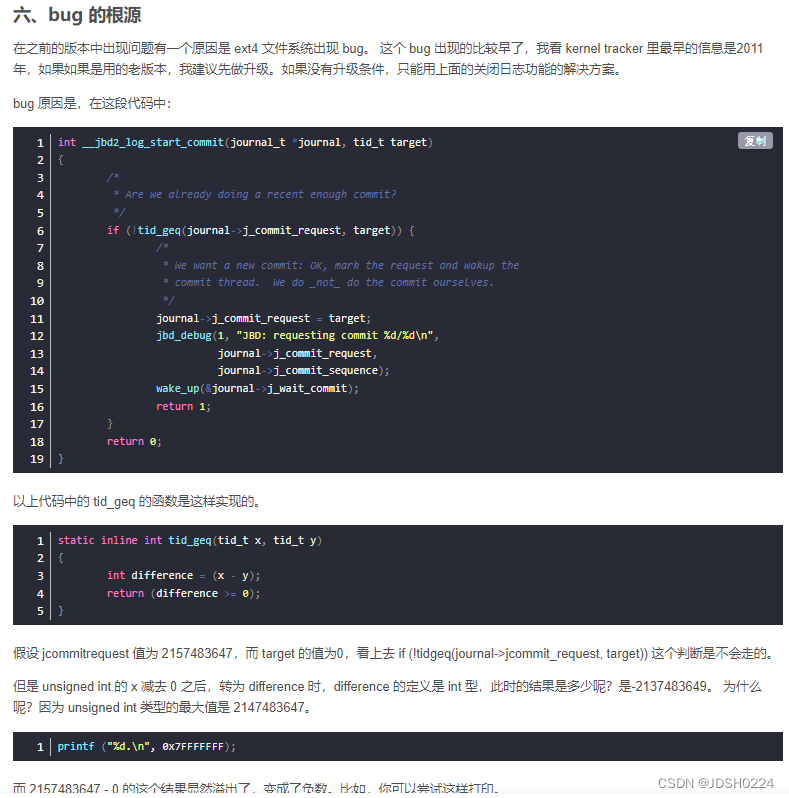
而本人的内核却是还存在这个bug
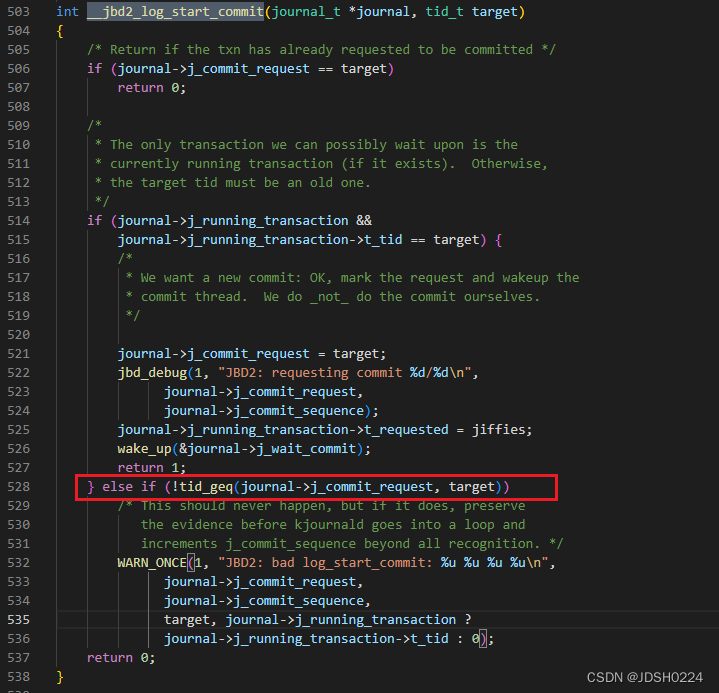
int jbd2_log_start_commit(journal_t *journal, tid_t tid)
{int ret;write_lock(&journal->j_state_lock);ret = __jbd2_log_start_commit(journal, tid);write_unlock(&journal->j_state_lock);return ret;
}
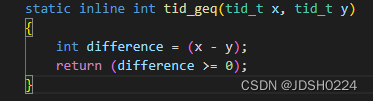
相关内容
热门资讯
安卓系统计划软件推荐,精选计划...
你有没有发现,手机里的安卓系统越来越智能了?这不,最近我可是挖到了一些超棒的安卓计划软件,它们不仅能...
收钱吧安卓系统插件,便捷支付新...
你有没有发现,现在的生活越来越离不开手机了?手机里装满了各种应用,而今天我要跟你聊聊一个特别实用的工...
鸿蒙系统是否还属于安卓,独立于...
你有没有想过,那个在我们手机上默默无闻的鸿蒙系统,它到底是不是安卓的“亲戚”呢?这个问题,估计不少手...
安卓系统手机用什么钱包,轻松管...
你有没有想过,你的安卓系统手机里装了那么多应用,但最离不开的,可能就是那个小小的钱包了。没错,就是那...
安卓系统能玩部落冲突吗,部落冲...
你有没有想过,安卓系统上的手机,是不是也能玩那款风靡全球的《部落冲突》呢?这款游戏自从推出以来,就吸...
智能机器人安卓系统,引领未来智...
你知道吗?在科技飞速发展的今天,智能机器人已经不再是科幻电影里的专属了。它们正悄悄地走进我们的生活,...
华为win10系统改装安卓系统...
你有没有想过,你的华为笔记本电脑里的Windows 10系统,能不能来个华丽变身,变成安卓系统呢?这...
旧电脑上安什么安卓系统,适配不...
你那台旧电脑是不是已经闲置好久了?别让它默默无闻地躺在角落里,给它来个华丽变身吧!今天,就让我来告诉...
安卓app语言跟随系统,随系统...
你知道吗?在手机世界里,有一个神奇的小功能,它就像你的贴身翻译官,无论你走到哪里,都能帮你轻松应对各...
惠城安卓系统降级在哪,揭秘降级...
你有没有遇到过手机系统升级后,发现新系统让你头疼不已,想回到那个熟悉的安卓系统呢?别急,今天就来告诉...
阿里云系统转安卓,揭秘安卓平台...
你知道吗?最近有个大动作在互联网圈里引起了不小的波澜,那就是阿里云系统竟然要转战安卓阵营了!这可不是...
安卓系统有最美壁纸么,探寻最美...
哦,亲爱的安卓用户,你是否曾在某个午后,百无聊赖地翻看着手机,突然被那一张张壁纸惊艳了眼眸?是的,我...
安卓系统采用Linux操作系统...
你知道吗?安卓系统,这个在我们手机上无处不在的小家伙,它的心脏竟然是Linux操作系统内核!是不是觉...
安卓原生平板通用系统,探索安卓...
你有没有发现,现在市面上平板电脑的品牌和型号真是五花八门,让人挑花了眼?不过,你知道吗?在众多安卓平...
小米1系统是安卓几,搭载安卓几...
你有没有想过,你的小米手机里那个熟悉的系统,其实是基于安卓的哦!没错,就是那个全球最流行的手机操作系...
可以安装安卓系统的相机,智能摄...
你有没有想过,一台相机不仅能拍出美美的照片,还能像智能手机一样,玩转各种应用?没错,现在市面上就有这...
安卓系统gps定位不准,安卓G...
你是不是也遇到过这种情况?手机里的安卓系统GPS定位总是不准,让人头疼不已。有时候,你明明就在家附近...
电信机顶盒装安卓系统,开启智能...
你有没有想过,家里的电信机顶盒其实也可以装上安卓系统呢?听起来是不是有点不可思议?别急,让我带你一步...
安卓系统可以做苹果桌面,打造个...
你知道吗?现在科技的发展真是让人眼花缭乱,竟然有人想出了安卓系统可以做苹果桌面的神奇想法!是不是觉得...
安卓系统自带的网页,功能与特色...
你有没有发现,每次打开安卓手机,那熟悉的系统界面里总有一个默默无闻的小家伙——安卓系统自带的网页浏览...
