手写promise原理系列四:封装Promise.prototype.then方法,promise.then的用法
文章目录
- 定义then方法
- (1)状态改变时,执行相应的回调函数,获取相应的结果数据
- (2)当异步执行更改 promise 状态时,缓存这两个回调函数,等待时机执行
- (3)当为 then 指定多个回调函数时,如何调用?
- (4)同步任务下,then 方法返回的结果实现
- (5)异步任务下,then 方法返回的结果实现
- (6)then 中指定的回调函数其实是异步执行的,也就是所谓的微任务
- (7)then 方法以及 Promise 构造函数的完整代码
这篇文章我们将封装 Promise.prototype.then 方法。
then 方法的封装逻辑比较复杂,所以这篇文章有点长,还请大家一定要耐心看完,相信你一定会有所收获的。若能将本系列通关,相信你的实力一定会再上一个台阶的,加油。
在 then 方法中,将实现以下功能:
- 执行 onResolved 以及 onRejected 回调函数的时机,成功时执行 onResolved,失败时执行 onResolved;
- pending 状态时,如何执行回调函数?
- 单次调用 then 方法时,如何缓存回调函数?
- 多次调用 then 方法时,如何缓存多个回调函数?
- then方法的返回值(同步、异步);
- then方法中回调函数是微任务;使用
queueMicrotask微任务队列。
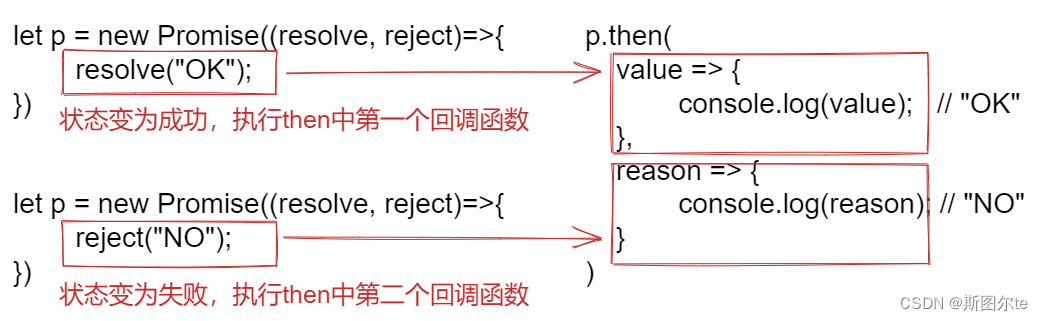
先来看 then 的使用方式:
let p = new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{resolve("OK");
})
p.then(value => {console.log(value); // "OK"
}, reason => {console.log(reason);
})
定义then方法
then 方法接受两个参数,第一个参数为状态变为成功时的回调函数 onResolved,第二个参数为状态变为失败时的回调函数onRejected。
(1)状态改变时,执行相应的回调函数,获取相应的结果数据
Promise.prototype.then = function(onResolved, onRejected){// 当状态变为成功时,执行 onResolved 回调函数if (this.PromiseState === "fulfilled") {onResolved(this.PromiseResult); // 传入 promise 的结果}// 当状态变为失败时,执行 onRejected 回调函数if (this.PromiseState === "rejected") {onRejected(this.PromiseResult); // 传入 promise 的结果}
}
如下图,加深理解:
(2)当异步执行更改 promise 状态时,缓存这两个回调函数,等待时机执行
异步执行时更改 promise 状态代码如下:
let p = new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{// 添加 setTimeout 异步更改状态setTimeout(() => {resolve("OK");}, 1000)
})
p.then(value => {console.log(value); // 1s后执行当前回调函数,输出"OK"
}, reason => {console.log(reason);
})
当使用异步方式更改 promise 状态时,then 方法会优先执行,但是状态还未更改,处于 pending 状态,所以无法执行 then 方法中的回调函数,记住一点:永远是状态更改在前,then 中回调函数执行在后。这时候怎么办呢?将 then 中的回调函数缓存起来,等待状态变更时再执行,这样就可以获取到最终结果了。逻辑如下:
- 给 promise 对象新增一个 callback 属性,用来缓存 then 中的回调函数;
- 异步改变状态时,因为 pending 状态的存在,所以回调函数的执行时机是在改变状态之后立即执行;
- 增加 pending 状态的判断逻辑,修改 Promise 构造函数代码;
function Promise(excutor){this.PromiseState = "pending";this.promiseResult = undefined;// 初始化 callback 回调函数缓存this.callback = {};const resolve = (value) => {if (this.PromiseState !== "pending") return;this.PromiseState = "fulfilled";this.PromiseResult = value;// 当异步状态改变时,立即从callback中取出函数调用,获取结果if(this.callback.onResolved){this.callback.onResolved(this.PromiseResult)}}const reject = (reason) => {if (this.PromiseState !== "pending") return;this.PromiseState = "rejected";this.PromiseResult = reason;// 当异步状态改变时,立即从callback中取出函数调用,获取结果if(this.callback.onRejected){this.callback.onRejected(this.PromiseResult)}}try {excutor(resolve, reject);} catch (err) {reject(err);}
}
Promise.prototype.then = function(onResolved, onRejected){// 当状态变为成功时,执行 onResolved 回调函数if (this.PromiseState === "fulfilled") {onResolved(this.PromiseResult)}// 当状态变为失败时,执行 onRejected 回调函数if (this.PromiseState === "rejected") {onRejected(this.PromiseResult)}// 当状态为pending时,缓存回调函数if (this.PromiseState === "pending") {this.callback = { onResolved, onRejected }}
}
(3)当为 then 指定多个回调函数时,如何调用?
在第(2)步中,callback 是一个对象,里面仅存储了一个成功的回调以及一个失败的回调,这样封装会有问题;当指定多个回调函数时,我们封装的then方法中,前面的回调函数会被后面的覆盖掉。像下面这种使用方式:
let p = new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{setTimeout(() => {resolve("OK");}, 1000)
})
// then1
p.then(value => {console.log("111"); // 被覆盖,无法输出
}, reason => {console.log("222"); // 被覆盖,无法输出
})
// then2,then2中的回调函数会覆盖then1中的回调函数
p.then(value => {console.log("aaa"); // 输出 "aaa"
}, reason => {console.log("bbb"); // 输出 "bbb"
})
所以,这里需要做一下修改,将 callback 修改为数组,这样可以存储多个回调函数,然后在 promise 状态改变时,全部执行。修改代码如下:
function Promise(excutor){this.PromiseState = "pending";this.promiseResult = undefined;// 初始化 callback 为数组this.callback = [];const resolve = (value) => {if (this.PromiseState !== "pending") return;this.PromiseState = "fulfilled";this.PromiseResult = value;// 当异步状态改变时,循环获取当前回调函数并执行this.callback.forEach(item => {if(item.onResolved){item.onResolved(this.PromiseResult)}})}const reject = (reason) => {if (this.PromiseState !== "pending") return;this.PromiseState = "rejected";this.PromiseResult = reason;// 当异步状态改变时,循环获取当前回调函数并执行this.callback.forEach(item => {if(item.onRejected){item.onRejected(this.PromiseResult)}})}// ...其他代码...
}
Promise.prototype.then = function(onResolved, onRejected){// ...其他代码...// 当状态为 pending 时,缓存回调函数if (this.PromiseState === "pending") {this.callback.push({ onResolved, onRejected })}
}
(4)同步任务下,then 方法返回的结果实现
在上面实现的 then 方法中,还没有实际的返回值;如果你去调用一下封装的 then 方法,返回值是一个 undefined。
下面我们将封装 then方法的返回值 逻辑:
- then 方法返回的是一个 promise 对象;
return new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{}) - then 方法中回调函数的返回值,就是 onResolved / onRejected 调用后的返回值;

- 接下来,只需要判断 then 中回调函数的返回值 result 的情况就可以了。这里可以参考手写promise系列二:手写promise的关键逻辑梳理中的第四点。简单说一下就是三种情况:①throw抛出异常;②promise对象;③非promise对象的任意值。

若回调函数返回值是一个 promise 对象,则回调函数返回的 promise 对象的结果就是 then 方法返回的 promise 对象的结果。
接下来书写代码,来看成功的情况(失败的情况与成功逻辑一致):
Promise.prototype.then = function(onResolved, onRejected){// 返回一个 promise 对象return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {// 当状态变为成功时,执行 onResolved回调函数if (this.PromiseState === "fulfilled") {// throw抛出异常,使用 try...catch...捕获异常(第一种情况)try {// 获取回调函数的返回值let result = onResolved(this.PromiseResult);// 是一个 promise对象(第二种情况)if (result instanceof Promise) {result.then(value => { // promise可以调用 then方法,本质就是递归调用resolve(value);}, reason => {reject(reason);})} else {// 非 promise对象的任意值(第三种情况)resolve(result);}} catch (err) {// throw 抛出异常时,执行结果状态变为失败reject(err);}}// 当状态变为失败时,执行 onRejected回调函数if (this.PromiseState === "rejected") {// ...与 fulfilled 的代码逻辑一致,此处省略...}})
}
(5)异步任务下,then 方法返回的结果实现
异步任务,就是改变状态时使用了 setTimeout、setInterval 等异步任务队列。
let p = new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{setTimeout(() => {resolve("OK");}, 1000)
})
p.then(value => {console.log(value); // 1s后输出 "OK"
}, reason => {console.log(reason);
})
执行上面代码,p 的状态一直是 pending,直到1s后结束,状态变为 resolve。那 pending 状态下,如何处理 then 方法的返回值呢?这里其实跟第(4)步是一样的,也是判断那三种情况,只是这次需要判断的内容是 callback 中缓存的回调函数。代码如下:
Promise.prototype.then = function(onResolved, onRejected){// 返回一个 promise 对象return new Promise((resolve,reject) => {// ...其他代码...// 当状态为 pending时,缓存回调函数if (this.PromiseState === "pending") {this.callback.push({onResolved: function(){// throw 抛出异常,使用 try...catch...捕获异常(第一种情况)try {// 获取回调函数的返回值let result = onResolved(this.PromiseResult);// 是一个 promise 对象(第二种情况)if (result instanceof Promise) {result.then(value => { // 这里调用then,本质就是递归resolve(value);}, reason => {reject(reason);})} else {// 非 promise 对象的任意值(第三种情况)resolve(result);}} catch (err) {reject(err);}}onRejected: function(){// ...与 onResolved 的代码逻辑一致,此处省略...}})}})
}
写到这里,我们可以看出,判断then方法的返回值的逻辑是有很大一部分重复的,这时候我们可以封装成一个公共方法。如下:
Promise.prototype.then = function(onResolved, onRejected){return new Promise((resolve,reject) => {// 公共逻辑封装成公共方法 getThenCallbackResult:获取回调函数的返回值const getThenCallbackResult = (type) => {try {// type 是一个函数let result = type(this.PromiseResult);if (result instanceof Promise) {result.then(value => {resolve(value);}, reason => {reject(reason);})} else {resolve(result);}} catch (err) {reject(err);}}if (this.PromiseState === "fulfilled") {getThenCallbackResult(onResolved);}if (this.PromiseState === "rejected") {getThenCallbackResult(onRejected);}if (this.PromiseState === "pending") {this.callback.push({onResolved: function(){getThenCallbackResult(onResolved);},onRejected: function(){getThenCallbackResult(onRejected);}})}})
}
(6)then 中指定的回调函数其实是异步执行的,也就是所谓的微任务
你知道下面代码所输出值的顺序么?真实的输出顺序其实是先输出 "111" ,然后输出 "333",最后输出 "222"。这里说明,其实 then 中的回调函数是一个微任务,所以要在同步代码执行完毕后,再执行回调函数。
let p = new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{resolve("111");
})
p.then(value => {console.log("222")
})
console.log("333");
在我们封装的代码中应该如何写出这种效果呢?很简单,将then中的回调函数全部放入微任务队列。请看代码:
Promise.prototype.then = function(onResolved, onRejected){return new Promise((resolve,reject) => {// ... 其他代码if (this.PromiseState === "fulfilled") {// 加入微任务队列,延迟执行queueMicrotask(() => {getThenCallbackResult(onResolved);}) }if (this.PromiseState === "rejected") {// 加入微任务队列,延迟执行queueMicrotask(() => {getThenCallbackResult(onRejected);})}if (this.PromiseState === "pending") {this.callback.push({onResolved: function(){// 加入微任务队列,延迟执行queueMicrotask(() => {getThenCallbackResult(onResolved);})},onRejected: function(){// 加入微任务队列,延迟执行queueMicrotask(() => {getThenCallbackResult(onRejected);})}})}})
}
(7)then 方法以及 Promise 构造函数的完整代码
function Promise(excutor){this.PromiseState = "pending";this.promiseResult = undefined;this.callback = [];const resolve = (value) => {if (this.PromiseState !== "pending") return;this.PromiseState = "fulfilled";this.PromiseResult = value;this.callback.forEach(item => {if(item.onResolved){item.onResolved()}})}const reject = (reason) => {if (this.PromiseState !== "pending") return;this.PromiseState = "rejected";this.PromiseResult = reason;this.callback.forEach(item => {if(item.onRejected){item.onRejected()}})}try {excutor(resolve, reject);} catch (err) {reject(err);}
}
Promise.prototype.then = function(onResolved, onRejected){return new Promise((resolve,reject) => {const getThenCallbackResult = (type) => {try {let result = type(this.PromiseResult);if (result instanceof Promise) {result.then(value => {resolve(value);}, reason => {reject(reason);})} else {resolve(result);}} catch (err) {reject(err);}}if (this.PromiseState === "fulfilled") {getThenCallbackResult(onResolved);}if (this.PromiseState === "rejected") {getThenCallbackResult(onRejected);}if (this.PromiseState === "pending") {this.callback.push({onResolved: function(){getThenCallbackResult(onResolved);},onRejected: function(){getThenCallbackResult(onRejected);}})}})
}
终于完成了本篇,我也长吁了一口气,第一次写这么长的文章。本篇文章确实有点小复杂,但相信大家多看多写,一定能攻克当前难点的,大家一定要先通关本系列的第一篇和第二篇文章,并理解其中字句真意。
其实上面的代码还有一点小瑕疵,就是当then中参数减少或不传入参数时,程序是会报错的,因为没有做兼容性处理,碍于本章篇幅过长,放到下一章与 catch 的 异常穿透 一起讲解。
下一篇:Python并发编程理论篇
