【数据结构】C语言实现栈和队列
创始人
2024-05-06 02:20:07
0次
目录
一、栈
1、栈的概念及结构
2、如何实现栈
3、代码实现
3.1 栈的定义
3.2 栈中将要实现的函数
3.3 函数实现
二、队列
1、队列的概念及结构
2、如何实现队列
3、代码实现
3.1 队列定义
3.2 队列中将要实现的函数
3.3 函数实现
一、栈
1、栈的概念及结构
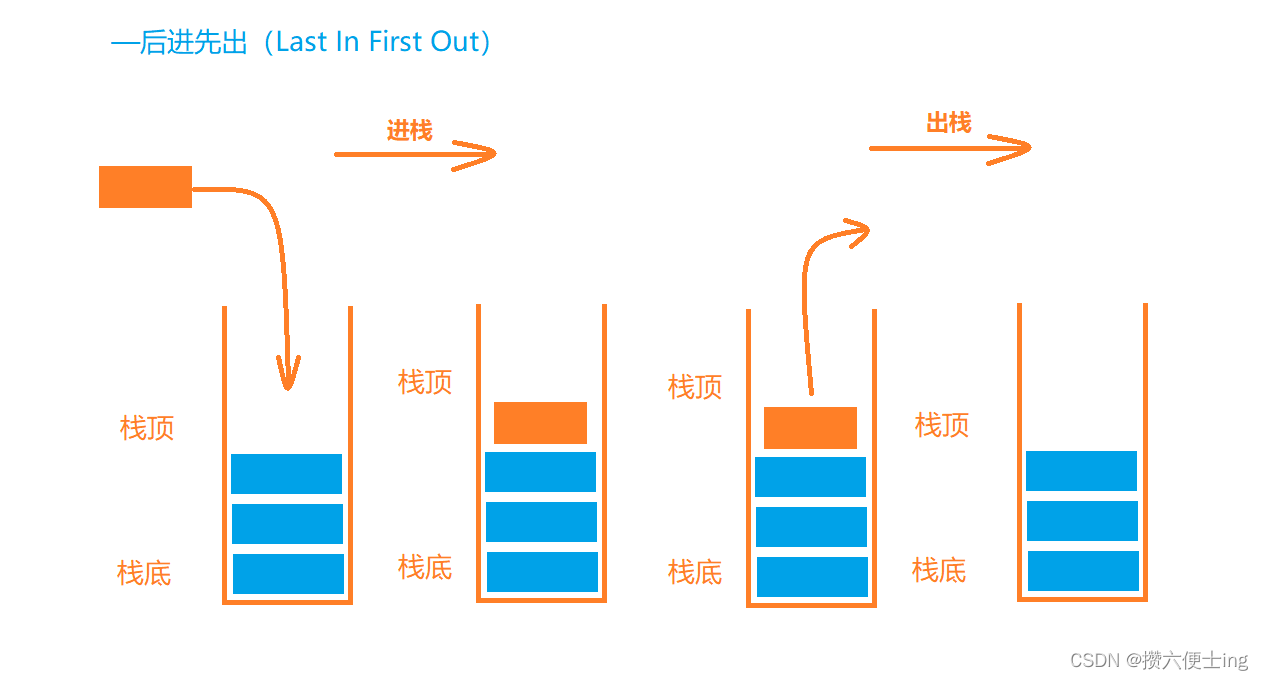
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称作栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的元素遵守后进先出LIFO(Last In Fisrt Out)的原则。
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据也在栈顶。
2、如何实现栈
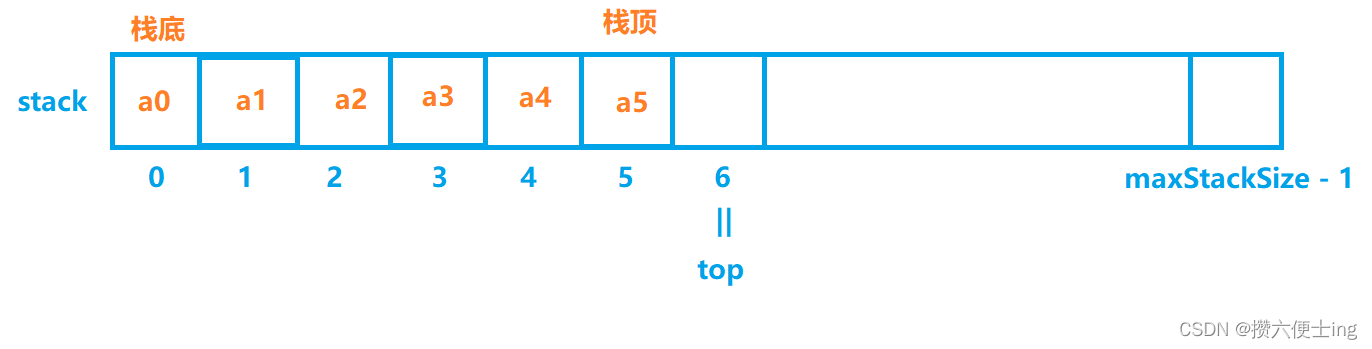
栈作为线性表的一种,实现方式无非两种。一种基于数组实现的顺序结构,另一种则基于链表实现。相对而言我们在实现栈的结构时更倾向于用数组实现,数组结构实现起来更优,因为数组在尾上插入数据的代价比较小。
3、代码实现
3.1 栈的定义
#include
#include
#include
#include typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{STDataType* data; //动态数组实现int size; //栈中有效数据个数int capacity; //栈的容量
}ST; 3.2 栈中将要实现的函数
//初始化队列
void StackInit(ST* ps);// 入栈
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);// 出栈
void StackPop(ST* ps);// 获取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps);// 获取栈中有效元素个数
int StackSize(ST* ps);// 检测栈是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果不为空返回0
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps);// 销毁栈
void StackDestroy(ST* ps);3.3 函数实现
//栈的初始化
void StackInit(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);int newcapacity = 4; //初识容量设置为4STDataType* a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * newcapacity);if (a == NULL){perror("malloc fail");exit(-1);}ps->data = a;ps->size = 0;//初识化为零,代表的是栈顶元素的下一个位置,同时也表示栈内的元素个数ps->capacity = newcapacity;
}//压栈操作,将元素压入栈中
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{assert(ps);if (ps->size == ps->capacity){//如果栈中元素有效个数已经达到容量大小,就进行扩容STDataType* a = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->data, 2 * ps->capacity * sizeof(STDataType));if (a == NULL){perror("realloc fail");exit(-1);}ps->data = a;ps->capacity *= 2;}ps->data[ps->size] = x;ps->size++;
}//出栈,将栈顶元素弹出
void StackPop(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);//防止栈中没有元素仍进行出栈操作//如果对空栈进行出栈,下一次进栈就会造成越界问题assert(ps->size > 0);ps->size--;
}//取出栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->data[ps->size - 1];
}//返回栈中元素个数
int StackSize(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->size;
}//判断栈是否为空栈
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->size == 0;
}//销毁栈
void StackDestroy(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);free(ps->data);ps->data = NULL;ps->capacity = ps->size = 0;
}二、队列
1、队列的概念及结构
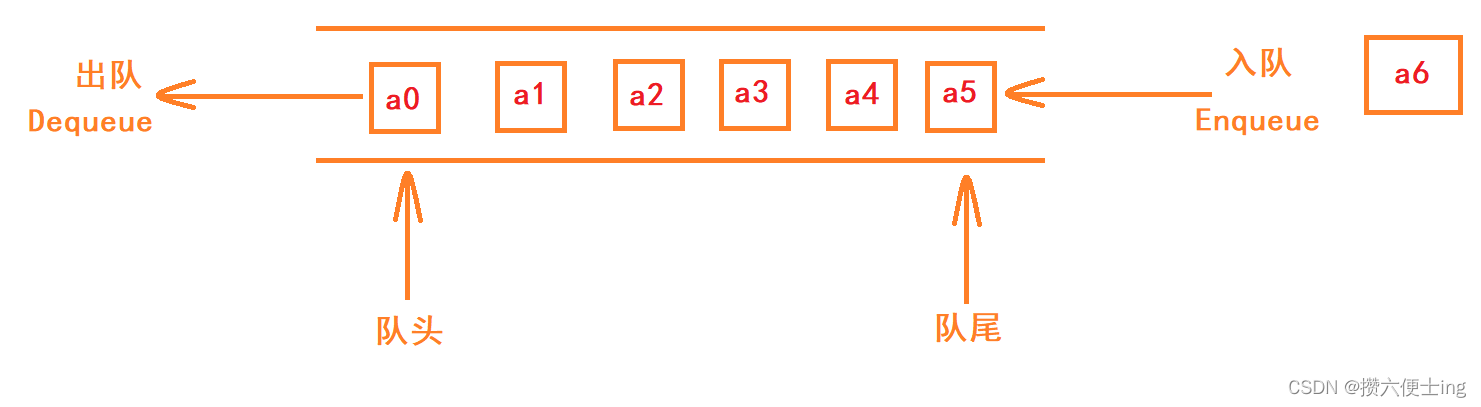
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列中的元素具有先进先出(First In First Out)原则。
入队列:进行插入操作一端称为队尾。
出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头。
2、如何实现队列
队列也可以数组和链表的结构实现,使用链表的结构实现更优一些,因为如果使用数组的结构,出队列在数组头上出数据,出完数据后需要挪动数据,效率会比较低。

3、代码实现
3.1 队列定义
#include
#include
#include
#include typedef int QDataType;
// 链式结构:表示队列
typedef struct QListNode
{struct QListNode* next;QDataType data;
}QNode;// 队列的结构
typedef struct Queue
{QNode* front; //队头QNode* rear; //队尾int size; //队列元素个数
}Queue; 3.2 队列中将要实现的函数
// 初始化队列
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);// 队尾入队列
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType data);// 队头出队列
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);// 获取队列头部元素
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);// 获取队列队尾元素
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);// 获取队列中有效元素个数
int QueueSize(Queue* pq);// 检测队列是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果非空返回0
int QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);// 销毁队列
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);3.3 函数实现
#include "Queue.h"
//初识化队列
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);pq->front = pq->rear = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}//入队列
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType data)
{assert(pq);QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc fail");exit(-1);}newnode->data = data;newnode->next = NULL;if (pq->front == NULL){pq->front = pq->rear = newnode;}else{pq->rear->next = newnode;pq->rear = newnode;}pq->size++;
}//出队列
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));if (pq->front->next == NULL){free(pq->front);pq->front = pq->rear = NULL;}else{QNode* next = pq->front->next;free(pq->front);pq->front = next;}pq->size--;
}//取队头元素
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));return pq->front->data;
}//取队尾元素
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));return pq->rear->data;
}//返回队列中元素个数
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->size;
}//判断队列是否为空
int QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->front == NULL && pq->rear == NULL;
}//销毁队列
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(pq->size > 0);QNode* cur = pq->front;while (cur){QNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}pq->size = 0;pq->front = pq->rear = NULL;
}以上就是通过C语言实现的栈和队列了,希望能够帮到大家,如果有不对的地方请各位大佬评论区指正。
上一篇:15.2 浏览器中的进程
下一篇:Java语法:枚举
相关内容
热门资讯
安卓系统自带的网页,功能与特色...
你有没有发现,每次打开安卓手机,那熟悉的系统界面里总有一个默默无闻的小家伙——安卓系统自带的网页浏览...
美咖云系统安卓版,开启智能生活...
你有没有发现,最近手机上多了一个叫“美咖云系统安卓版”的小家伙?它就像一个魔法师,轻轻一点,就能让你...
安卓系统推荐最好的手机,盘点性...
你有没有想过,拥有一部性能卓越的手机,就像是拥有了移动的宝藏库?在这个信息爆炸的时代,一部好手机不仅...
安卓11系统能精简吗,释放潜能
你有没有发现,随着手机越来越智能,系统也越来越庞大?安卓11系统,这个最新的操作系统,是不是也让你觉...
安卓自动重启系统软件,揭秘原因...
手机突然自动重启,是不是感觉整个人都不好了?别急,今天就来和你聊聊这个让人头疼的安卓自动重启系统软件...
苹果手机x刷安卓系统,探索安卓...
你有没有想过,你的苹果手机X竟然也能刷上安卓系统?是的,你没听错,就是那个一直以来都和我们苹果手机X...
安卓系统智商低吗,智商低下的真...
你有没有想过,为什么安卓系统的智商总被调侃得好像有点低呢?是不是觉得它总是慢吞吞的,有时候还犯点小错...
安卓系统手机联系人,揭秘你的社...
你有没有发现,手机里的联系人列表就像是一个小小的社交圈呢?里面藏着我们的亲朋好友、工作伙伴,甚至还有...
安卓系统免费铃声下载,打造个性...
手机里那首老掉牙的铃声是不是让你觉得有点out了呢?别急,今天就来给你支个招,让你轻松给安卓手机换上...
安卓系统用哪个桌面好,打造个性...
你有没有发现,手机桌面可是我们每天都要面对的“脸面”呢?换一个好看的桌面,心情都能跟着好起来。那么,...
虚拟大师是安卓10系统,功能与...
你知道吗?最近在手机圈里,有个新玩意儿引起了不小的轰动,那就是虚拟大师!而且,更让人惊喜的是,这个虚...
安卓系统与苹果优缺点,系统优缺...
说到手机操作系统,安卓和苹果绝对是两大巨头,它们各有各的特色,就像两道不同的美味佳肴,让人难以抉择。...
安卓win双系统主板,融合与创...
你有没有想过,一台电脑如果既能流畅运行安卓系统,又能轻松驾驭Windows系统,那该有多爽啊?没错,...
安卓系统可精简软件,轻松提升手...
你有没有发现,手机里的安卓系统越来越庞大,软件也越装越多,有时候感觉手机就像个“大肚子”,不仅运行速...
安卓系统基于linux的代码,...
你有没有想过,那个陪伴你每天刷抖音、玩游戏、办公的安卓系统,其实背后有着一套复杂的基于Linux的代...
苹果和安卓的拍照系统,谁更胜一...
你有没有发现,现在手机拍照已经成为我们生活中不可或缺的一部分呢?无论是记录生活的点滴,还是捕捉美丽的...
苹果和安卓系统不同吗,系统差异...
你有没有想过,为什么你的手机里装的是苹果的iOS系统,而朋友的手机却是安卓系统呢?这两种系统,看似都...
安卓系统有多少级,揭秘其多级架...
你有没有想过,那个陪伴我们日常生活的安卓系统,它其实有着丰富的层级结构呢?没错,就是那个让我们的手机...
华为鸿蒙系统与安卓的,技术融合...
你知道吗?最近科技圈可是炸开了锅,华为鸿蒙系统与安卓的较量成为了大家热议的话题。这不,今天我就来给你...
什么安卓手机是苹果系统,搭载苹...
你有没有想过,为什么有些人宁愿花大价钱买苹果手机,而有些人却对安卓手机情有独钟呢?其实,这个问题背后...
